Austria
Republic of Austria Republik Österreich (German) | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "Bundeshymne der Republik Österreich" "National Anthem of the Republic of Austria" | |
Location of Austria (dark green) – in Europe (green & dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Vienna 48°12′N 16°21′E / 48.200°N 16.350°E |
| Official languages | German[a][b] |
| National language | Austrian German (Austrian)[c] |
| Official regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2023)[3] | |
| Religion (2021)[4] |
|
| Demonym(s) | Austrian |
| Government | Federal semi-presidential parliamentary republic[5][d] |
| Alexander Van der Bellen | |
| Karl Nehammer | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Federal Council | |
| National Council | |
| Formation | |
| c. 970 (1 November 996) | |
• Duchy | 17 September 1156 |
| 6 January 1453 | |
| 1512 | |
• Empire | 11 August 1804 |
| 30 March 1867 | |
| 10 September 1919 | |
| 1 May 1934 | |
| 13 March 1938 | |
| 27 April 1945 | |
| 27 July 1955 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 83,879[8] km2 (32,386 sq mi) (113th) |
• Water (%) | 0.84 (2015)[9] |
| Population | |
• April 2022 estimate | |
• Density | 107.6/km2 (278.7/sq mi) (106th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2023) | low inequality |
| HDI (2022) | very high (22nd) |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | +43 |
| ISO 3166 code | AT |
| Internet TLD | .at |
Austria,[e] formally the Republic of Austria,[f] is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps.[15] It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of 83,879 km2 (32,386 sq mi) and has a population of around 9 million.[10]
The area of today's Austria has been inhabited since at least the Paleolithic period. Around 400 BC, it was inhabited by the Celts and then annexed by the Romans in the late 1st century BC. Christianization in the region began in the 4th and 5th centuries, during the late Roman period, followed by the arrival of numerous Germanic tribes during the Migration Period.[16] Austria, as a unified state, emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium, first as a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, it then developed into a Duchy in 1156, and was made an Archduchy in 1453. Being the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy since the late 13th century, Austria was a major imperial power in Central Europe for centuries and from the 16th century, Vienna was also serving as the Holy Roman Empire's administrative capital.[17] Before the dissolution of the empire two years later, in 1804, Austria established its own empire, which became a great power and one of the largest states in Europe. The empire's defeat in wars and the loss of territories in the 1860s paved the way for the establishment of Austria-Hungary in 1867.[18]
After the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in 1914, Emperor Franz Joseph declared war on Serbia, which ultimately escalated into World War I. The empire's defeat and subsequent collapse led to the proclamation of the Republic of German-Austria in 1918 and the First Austrian Republic in 1919. During the interwar period, anti-parliamentarian sentiments culminated in the formation of an Austrofascist dictatorship under Engelbert Dollfuss in 1934. A year before the outbreak of World War II, Austria was annexed into Nazi Germany by Adolf Hitler, and it became a sub-national division. After its liberation in 1945 and a decade of Allied occupation, the country regained its sovereignty and declared its perpetual neutrality in 1955.
Austria is a semi-presidential parliamentary[d] representative democracy with a popularly elected president as head of state and a chancellor as head of government and chief executive. Austria has the 13th highest nominal GDP per capita with high standards of living. The country has been a member of the United Nations since 1955[19] and of the European Union since 1995.[20] It hosts the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) and the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and is a founding member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and Interpol.[21] It also signed the Schengen Agreement in 1995,[22] and adopted the euro currency in 1999.[23]
Etymology
The native name for Austria, Österreich, derives from the Old High German Ostarrîchi, which meant "eastern realm" and which first appeared in the "Ostarrîchi document" of 996.[24][25] This word is probably a translation of Medieval Latin Marchia orientalis into a local (Bavarian) dialect.
Austria was a prefecture of Bavaria created in 976. The word "Austria" is a Latinisation of the German name and was first recorded in the 12th century.[26] At the time, the Danube basin of Austria (Upper and Lower Austria) was the easternmost extent of Bavaria.
History
Prehistory and antiquity

The area that is now Austria was settled in pre-Roman times by various Celtic tribes, having been the core of the Hallstatt culture by the 6th century BC.[27] The city of Hallstatt, in fact, has the oldest archaeological evidence of the Celts in Europe.[28]
The Celtic Kingdom of Noricum that included most of modern Austria and parts of modern Slovenia was conquered by the Roman Empire in 16 BC and made a province called Noricum which lasted until the year of 476.[29] The regions of today's Austria which were not located within the province of Noricum were divided between the Roman provinces of Pannonia, which encompassed parts of eastern Austria, and Raetia, which encompassed the areas of present-day Vorarlberg and Tyrol.[30][31]
Present-day Petronell-Carnuntum in eastern Austria was an important army camp turned capital city in what became known as the Pannonia Superior. Carnuntum was home to 50,000 people for nearly 400 years.[32]
Middle Ages
After the fall of the Roman Empire, the area was first invaded by the Germanic Rugii which made this region part of their "Rugiland".[33] In 487, most of modern Austria was conquered by Odoacer, a barbarian soldier and statesman from the Middle Danube, which incorporated most of today's Austria in his Kingdom of Italy. By 493, it was conquered by the Germanic Ostrogoths which created their own kingdom, the Ostrogothic Kingdom.[34] Following the Kingdom's fall the area was invaded by the Alemanni, Baiuvarii, Slavs, and Avars.[35][36]
Charlemagne, King of the Franks, conquered the area in 788, encouraged colonisation, and introduced Christianity.[35] As part of Eastern Francia, the core areas that now encompass Austria were bequeathed to the house of Babenberg. The area was known as the marchia Orientalis and was given to Leopold of Babenberg in 976.[37]
The first record showing the name Austria is from 996, where it is written as Ostarrîchi, referring to the territory of the Babenberg March.[37] In 1156, the Privilegium Minus elevated Austria to the status of a duchy. In 1192, the Babenbergs also acquired the Duchy of Styria. With the death of Frederick II in 1246, the line of the Babenbergs was extinguished.[38]
As a result, Ottokar II of Bohemia effectively assumed control of the duchies of Austria, Styria, and Carinthia.[38] His reign came to an end with his defeat at Dürnkrut at the hands of Rudolph I of Germany in 1278.[39] Thereafter, until World War I, Austria's history was largely that of its ruling dynasty, the Habsburgs.
In the 14th and 15th centuries, the Habsburgs began to accumulate other provinces in the vicinity of the Duchy of Austria. In 1438, Duke Albert V of Austria was chosen as the successor to his father-in-law, Emperor Sigismund. Although Albert himself only reigned for a year, henceforth every emperor of the Holy Roman Empire was a Habsburg, with only one exception.
The Habsburgs began also to accumulate territory far from the hereditary lands. In 1477, Archduke Maximilian, only son of Emperor Frederick III, married the heiress Maria of Burgundy, thus acquiring most of the Netherlands for the family.[40][41] In 1496, his son Philip the Fair married Joanna the Mad, the heiress of Castile and Aragon, thus acquiring Spain and its Italian, African, Asian, and New World appendages for the Habsburgs.[40][41]
In 1526, following the Battle of Mohács, Bohemia and the part of Hungary not occupied by the Ottomans came under Austrian rule.[42] Ottoman expansion into Hungary led to frequent conflicts between the two empires, particularly evident in the Long War of 1593 to 1606. The Turks made incursions into Styria nearly 20 times,[43] of which some are cited as "burning, pillaging, and taking thousands of slaves".[44] In late September 1529, Suleiman the Magnificent launched the first siege of Vienna, which unsuccessfully ended, according to Ottoman historians, with the snowfalls of an early beginning winter.
17th and 18th centuries

During the long reign of Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor following the successful defence of Vienna against the Turks in 1683, under the command of the King of Poland John III Sobieski,[45] the Great Turkish War resulted in most of Hungary being controlled by Austria. This arrangement was formalized in the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699.
Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor relinquished many of the gains the empire made in the previous years. He enjoyed the imminent extinction of the House of Habsburg. Charles VI was willing to offer concrete advantages in territory and authority in exchange for recognition of the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713. Therefore, his daughter Maria Theresa was recognized as his heir. With the rise of Prussia, the Austria–Prussia rivalry began in Germany. Austria participated, together with Prussia and Russia, in the first and the third of the three Partitions of Poland in 1772 and 1795 respectively.
From that time, Austria became the birthplace of classical music and played host to different composers including Joseph Haydn, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Ludwig van Beethoven, and Franz Schubert.
19th century
Austria later became engaged in a war with Revolutionary France, which was highly unsuccessful in the beginning, with successive defeats at the hands of Napoleon Bonaparte, meaning the end of the old Holy Roman Empire in 1806. Two years earlier,[46] the Empire of Austria was founded. From 1792 to 1801, the Austrians had suffered 754,700 casualties.[47] In 1814, Austria was part of the Allied forces that invaded France and brought to an end the Napoleonic Wars.
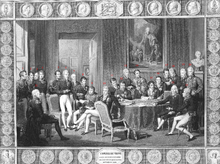
It emerged from the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as one of the continent's four dominant powers and a recognised great power. The same year, the German Confederation (Deutscher Bund) was founded under the presidency of Austria. Because of unsolved social, political, and national conflicts, the German lands were shaken by the 1848 revolutions aiming to create a unified Germany.[48]
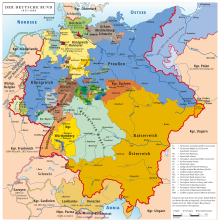
The various different possibilities for a united Germany were: a Greater Germany, or a Greater Austria or just the German Confederation without Austria at all. As Austria was not willing to relinquish its German-speaking territories to what would become the German Empire of 1848, the crown of the newly formed empire was offered to the Prussian King Friedrich Wilhelm IV. In 1864, Austria and Prussia fought together against Denmark and secured the independence from Denmark of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein. As they could not agree on how the two duchies should be administered, though, they fought the Austro-Prussian War in 1866. Defeated by Prussia in the Battle of Königgrätz,[48] Austria had to leave the German Confederation and no longer took part in German politics.[49][50]
After the defeated Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, the Ausgleich, provided for a dual sovereignty, the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary, under Franz Joseph I.[51] The Austrian-Hungarian rule of this diverse empire included various groups, including Germans, Hungarians, Croats, Czechs, Poles, Rusyns, Serbs, Slovaks, Slovenes, and Ukrainians, as well as large Italian and Romanian communities.
As a result, ruling Austria-Hungary became increasingly difficult in an age of emerging nationalist movements, requiring considerable reliance on an expanded secret police. Yet, the government of Austria tried its best to be accommodating in some respects: for example, the Reichsgesetzblatt, publishing the laws and ordinances of Cisleithania, was issued in eight languages; and all national groups were entitled to schools in their own language and to the use of their mother tongue at state offices.
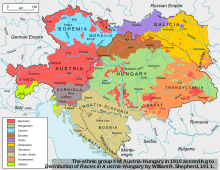
Many Austrian Germans of all different social circles such as Georg Ritter von Schönerer promoted strong pan-Germanism in the hope of reinforcing an ethnic German identity amongst Austrian Germans and the annexation of Austria to Germany (Anschluss).[52] Some Austrians such as Karl Lueger also used pan-Germanism as a form of populism to further their own political goals. Although Bismarck's policies excluded Austria and the German Austrians from Germany, many Austrian pan-Germans idolised him and wore blue cornflowers, known to be the favourite flower of German Emperor William I, in their buttonholes, along with cockades in the German national colours (black, red, and yellow), although they were both temporarily banned in Austrian schools, as a way to show discontent towards the multi-ethnic empire.[53]
Austria's exclusion from Germany caused many Austrians a problem with their national identity and prompted the Social Democratic Leader Otto Bauer to state that it was "the conflict between our Austrian and German character".[54] The Austro-Hungarian Empire caused ethnic tension between the German Austrians and the other ethnic groups. Many Austrians, especially those involved with the pan-German movements, desired a reinforcement of an ethnic German identity and hoped that the empire would collapse, which would allow an annexation of Austria by Germany.[55]
A lot of Austrian pan-German nationalists protested passionately against minister-president Kasimir Count Badeni's language decree of 1897, which made German and Czech co-official languages in Bohemia and required new government officials to be fluent in both languages. This meant in practice that the civil service would almost exclusively hire Czechs because most middle-class Czechs spoke German but not the other way around. The support of ultramontane Catholic politicians and clergy for this reform triggered the launch of the Away from Rome movement, which was initiated by supporters of Schönerer and called on "German" Christians to leave the Roman Catholic Church.[56]
Early 20th century
As the Second Constitutional Era began in the Ottoman Empire, Austria-Hungary took the opportunity to annex Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1908.[57] The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo in 1914 by Bosnian Serb Gavrilo Princip[58] was used by leading Austrian politicians and generals to persuade the emperor to declare war on Serbia, thereby risking and prompting the outbreak of World War I, which eventually led to the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Over one million Austro-Hungarian soldiers died in World War I.[59]

On 21 October 1918, the elected German members of the Reichsrat (parliament of Imperial Austria) met in Vienna as the Provisional National Assembly for German Austria (Provisorische Nationalversammlung für Deutschösterreich). On 30 October the assembly founded the Republic of German-Austria by appointing a government, called Staatsrat. This new government was invited by the Emperor to take part in the decision on the planned armistice with Italy but refrained from this business.[60]
This left the responsibility for the end of the war, on 3 November 1918, solely to the emperor and his government. On 11 November, the emperor, advised by ministers of the old and the new governments, declared he would not take part in state business any more; on 12 November, German-Austria, by law, declared itself to be a democratic republic and part of the new German republic. The constitution, renaming the Staatsrat as Bundesregierung (federal government) and Nationalversammlung as Nationalrat (national council) was passed on 10 November 1920.[61]
The Treaty of Saint-Germain of 1919 (for Hungary the Treaty of Trianon of 1920) confirmed and consolidated the new order of Central Europe which to a great extent had been established in November 1918, creating new states and altering others. The German-speaking parts of Austria which had been part of Austria-Hungary were reduced to a rump state named the Republic of German-Austria (German: Republik Deutschösterreich), though excluding the predominantly German-speaking South Tyrol.[62][63][64] The desire for the annexation of Austria to Germany was a popular opinion shared by all social circles in both Austria and Germany.[65] On 12 November, German-Austria was declared a republic, and named Social Democrat Karl Renner as provisional chancellor. On the same day it drafted a provisional constitution that stated that "German-Austria is a democratic republic" (Article 1) and "German-Austria is an integral part of the German reich" (Article 2).[66] The Treaty of Saint Germain and the Treaty of Versailles explicitly forbade union between Austria and Germany.[67][68] The treaties also forced German-Austria to rename itself as "Republic of Austria" which consequently led to the first Austrian Republic.[69][70]
Over three million German-speaking Austrians found themselves living outside the new Austrian Republic as minorities in the newly formed or enlarged states of Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Hungary, and Italy.[71] These included the provinces of South Tyrol, and German Bohemia. The status of German Bohemia and Sudetenland later played a role in World War II.[72]
The border between Austria and the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was settled with the Carinthian Plebiscite in October 1920 and allocated the major part of the territory of the former Austro-Hungarian Crownland of Carinthia to Austria. This set the border on the Karavanke mountain range, with many Slovenes remaining in Austria.
Interwar period and World War II
After the war, inflation began to devalue the Krone, which was still Austria's currency. In the autumn of 1922, Austria was granted an international loan supervised by the League of Nations.[73] The purpose of the loan was to avert bankruptcy, stabilise the currency, and improve Austria's general economic condition. The loan meant that Austria passed from an independent state to the control exercised by the League of Nations. In 1925, the Austrian schilling was introduced, replacing the Krone at a rate of 10,000:1. Later, it was nicknamed the "Alpine dollar" due to its stability. From 1925 to 1929 the economy enjoyed a short high before nearly crashing after Black Tuesday.
The First Austrian Republic lasted until 1933, when Chancellor Engelbert Dollfuss, using what he called "self-switch-off of Parliament", established an autocratic regime tending towards Italian fascism.[74][75] The two big parties at this time, the Social Democrats and the Conservatives, had paramilitary armies;[76] the Social Democrats' Republikanischer Schutzbund was now declared illegal, but was still operative[76] as the 12–15 February 1934 Austrian Civil War broke out.[74][75][77]
In February 1934, several members of the Schutzbund were executed,[78] the Social Democratic party was outlawed, and many of its members were imprisoned or emigrated.[77] On 1 May 1934, the Austrofascists imposed a new constitution ("Maiverfassung") which cemented Dollfuss's power, but on 25 July he was assassinated in an Austrian Nazi coup attempt.[79][80]

His successor Kurt Schuschnigg acknowledged the fact that Austria was a "German state" and he also believed that Austrians were "better Germans" but he wished that Austria would remain independent.[81] He announced a referendum on 9 March 1938, to be held on 13 March, concerning Austria's independence from Germany.
Nazi rule
On 12 March 1938, Austrian Nazis took over the government, while German troops occupied the country, which prevented Schuschnigg's referendum from taking place.[82] On 13 March 1938, the Anschluss (lit. 'joining' or 'connection') of Austria was officially declared. Two days later, Austrian-born Adolf Hitler announced what he called the "reunification" of his home country with the "rest of the German Reich" on Vienna's Heldenplatz. He established a referendum which confirmed the union with Germany in April 1938.
Parliamentary elections were held in Germany (including recently annexed Austria) on 10 April 1938. They were the final elections to the Reichstag during Nazi rule, and they took the form of a single-question referendum asking whether voters approved of a single Nazi-party list for the 813-member Reichstag, as well as the recent annexation of Austria (the Anschluss). Jews, Roma and Sinti were not allowed to vote.[83] Turnout in the election was officially 99.5%, with 98.9% voting "yes". In the case of Austria, Adolf Hitler's native soil, 99.71% of an electorate of 4,484,475 officially went to the ballots, with a positive tally of 99.73 percent.[84] Although most Austrians favored the Anschluss, in certain parts of Austria, the German soldiers were not always welcomed with flowers and joy, especially in Vienna, which had Austria's largest Jewish population.[85] Nevertheless, despite the propaganda and the manipulation and rigging which surrounded the ballot box result, there was massive genuine support for Hitler for fulfilling the Anschluss,[86] since many Germans from both Austria and Germany saw it as completing the long overdue unification of all Germans into one state.[87]
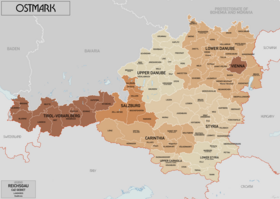
On 13 March 1938, Austria was annexed by the Third Reich and ceased to exist as an independent country (the Anschluss). The Aryanisation of the wealth of Jewish Austrians started immediately in mid-March, with a so-called "wild" (i.e. extra-legal) phase, but it was soon structured legally and bureaucratically so the assets which Jewish citizens possessed could be stripped from them. At that time, Adolf Eichmann, who grew up in Austria, was transferred to Vienna and ordered to persecute the Jews. During the November pogrom in 1938 ("Reichskristallnacht"), Jews and Jewish institutions such as synagogues were subjected to violent attacks in Vienna, Klagenfurt, Linz, Graz, Salzburg, Innsbruck and several cities in Lower Austria.[88][89][90][91][92] Otto von Habsburg, a vehement opponent of the Nazis, the last Crown Prince of Austria-Hungary, an honorary citizen of hundreds of places in Austria and partly envisaged by Schuschnigg as a monarchical option, was in Belgium at the time. He spoke out against the Anschluss and was then wanted by the Nazi regime and his property would have been expropriated and he would have been shot immediately if he were caught.[93] In 1938, the Nazis renamed Austria the "Ostmark",[82] a name which it had until 1942, when it was renamed the "Alpine and Danubian Gaue" (Alpen-und Donau-Reichsgaue).[94][95]
Though Austrians made up only 8% of the population of the Third Reich,[96] some of the most prominent Nazis were native Austrians, including Adolf Hitler, Ernst Kaltenbrunner, Arthur Seyss-Inquart, Franz Stangl, Alois Brunner, Friedrich Rainer, and Odilo Globocnik,[97] as were over 13% of the members of the SS and 40% of the staff at the Nazi extermination camps.[96] In the Reichsgau, besides the main camp KZ-Mauthausen, there were numerous sub-camps in all provinces where Jews and other prisoners were killed, tortured and exploited.[98] At this time, because the territory was outside the operational radius of Allied aircraft, the armaments industry was greatly expanded through the forced labor of concentration camp prisoners, this was especially the case with regard to the manufacture of fighter planes, tanks and missiles.[99][100][101]
Most of the resistance groups were soon crushed by the Gestapo. While the plans of the group around Karl Burian to blow up the Gestapo's headquarters in Vienna were uncovered,[102] the important group around the later executed priest Heinrich Maier managed to contact the Allies. This so-called Maier-Messner group was able to send the Allies information about armaments factories where V-1 flying bombs, V-2 rockets, Tiger tanks, and aircraft (Messerschmitt Bf 109, Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet, etc.) were manufactured, information which was important to the success of Operation Crossbow and Operation Hydra, both of which were preliminary missions before the launch of Operation Overlord. This resistance group, which was in contact with the American secret service (OSS), soon provided information about mass executions and concentration camps such as Auschwitz. The group's aim was to cause Nazi Germany to lose the war as quickly as possible and re-establish an independent Austria.[103][104][105]

Allied occupation
Vienna fell on 13 April 1945, during the Soviet Vienna offensive, just before the total collapse of the Third Reich. The invading Allied powers, in particular the Americans, planned for the supposed "Alpine Fortress Operation" of a national redoubt, that was largely to have taken place on Austrian soil in the mountains of the Eastern Alps. However, it never materialised because of the rapid collapse of the Reich.
Karl Renner and Adolf Schärf (Socialist Party of Austria [Social Democrats and Revolutionary Socialists]), Leopold Kunschak (Austria's People's Party [former Christian Social People's Party]), and Johann Koplenig (Communist Party of Austria) declared Austria's secession from the Third Reich by the Declaration of Independence on 27 April 1945 and set up a provisional government in Vienna under state Chancellor Renner the same day, with the approval of the victorious Red Army and backed by Joseph Stalin.[106] (The date is officially named the birthday of the second republic.) At the end of April, most of western and southern Austria were still under Nazi rule. On 1 May 1945, the Federal Constitutional Law of 1920, which had been terminated by dictator Dollfuss on 1 May 1934, was declared valid again. The total number of Austrian military deaths from 1939 to 1945 was 260,000.[107] The total number of Jewish Austrian Holocaust victims was 65,000.[108] About 140,000 Jewish Austrians had fled from the country in 1938–39. Thousands of Austrians had taken part in serious Nazi crimes (hundreds of thousands of people died in the Mauthausen-Gusen concentration camp alone), a fact which was officially acknowledged by Chancellor Franz Vranitzky in 1992.

Allied-occupied Austria was after World War II divided into military occupation zones. Austria was governed by the Allied Commission for Austria.[109] As stipulated in the Moscow Declaration of 1943 a subtle difference was seen in the treatment of Austria by the Allies.[106]
The Austrian government, consisting of Social Democrats, Conservatives, and Communists resided in Vienna, which was surrounded by the Soviet zone. This Austrian government was recognised by the allies of World War II in October 1945 despite concerns that Karl Renner could be Stalin's puppet.[110] On 26 July 1946 the Austrian Parliament passed its first nationalization law and approximately 70 mining and manufacturing companies were seized by the Austrian state. The Ministry of Property Protection and Economic Planning (Ministerium für Vermögenssicherung und Wirtschaftsplanung) was responsible for directing the nationalized industries under the directorship of Minister Peter Krauland (party ÖVP).[111]
Independence
On 15 May 1955, after talks which lasted for years and were influenced by the Cold War Austria regained full independence by concluding the Austrian State Treaty with the allies of World War II. On 26 October 1955, all occupation troops had left and Austria declared its permanent neutrality by an act of parliament.[112] This day is now Austria's National Day, a public holiday.[113]
The status of Tyrol was a lingering problem between Austria and Italy. To this day, there are 20 different squares in Austrian cities called "Südtiroler Platz" (South Tyrolean Square) in memory of the supposed loss of the Austrian territories. Terrorist acts by the South Tyrolean independence movement have been documented in the 1950s and 1960s. A great degree of autonomy was granted to Tyrol by the Italian national government.

The political system of the Second Republic is based on the constitution of 1920 and 1929, which was reintroduced in 1945. The system came to be characterised by Proporz, whereby most posts of political importance were split proportionately between members of the Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ) and the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP).[114] Interest group "chambers" with mandatory membership (e.g. for workers, business people, farmers) grew to considerable importance and were usually consulted in the legislative process, so hardly any legislation was passed that did not reflect widespread consensus.[115]
Since 1945, governing via a single-party government has occurred twice: 1966–1970 (ÖVP) and 1970-1983 (SPÖ). During all other legislative periods, either a grand coalition of SPÖ and ÖVP or a "small coalition" (one of these two and a smaller party) ruled the country.
Kurt Waldheim, the former secretary-general of the United Nations, was elected President of Austria from 1986 to 1992. He had been a Wehrmacht officer in the Second World War and was accused of war crimes.[116]
Following a referendum in 1994, at which consent reached a majority of two-thirds, the country became a member of the European Union on 1 January 1995.[117]
The major parties SPÖ and ÖVP have contrary opinions about the future status of Austria's military nonalignment: While the SPÖ in public supports a neutral role, the ÖVP argues for stronger integration into the EU's security policy; even a future NATO membership is not ruled out by some ÖVP politicians (ex. Werner Fasslabend (ÖVP) in 1997).[citation needed] In reality, Austria is taking part in the EU's Common Foreign and Security Policy, participates in peacekeeping and peace creating tasks, and has become a member of NATO's "Partnership for Peace"; the constitution has been amended accordingly.[118] Since Liechtenstein joined the Schengen Area in 2011, none of Austria's neighbouring countries performs border controls towards it anymore.[119]
Government and politics

The Parliament of Austria is located in Vienna, the country's capital and most populous city. Austria became a federal, representative democratic republic through the Federal Constitutional Law of 1920. The political system of the Second Republic with its nine federal states is based on the constitution of 1920, amended in 1929, which was re-enacted on 1 May 1945.[120]
The president of Austria is the head of state. The president is directly elected by popular majority vote, with a run-off between the top-scoring candidates if necessary. The chancellor of Austria is head of the government. The chancellor is selected by the president and tasked with forming a government based on the partisan composition of the lower house of parliament.
The government can be removed from office by either a presidential decree or by vote of no confidence in the lower chamber of parliament, the Nationalrat. Voting for the president and for the parliament used to be compulsory in Austria. The compulsion was abolished in steps from 1982 to 2004.[121]
Austria's parliament consists of two chambers. The composition of the Nationalrat (183 seats) is determined every five years (or whenever the Nationalrat has been dissolved by the federal president on a motion by the federal chancellor, or by the Nationalrat itself) by a general election in which every citizen over the age of 16 has the right to vote. The voting age was lowered from 18 in 2007.[122]
While there is a general threshold of 4% of the vote for all parties in federal elections (Nationalratswahlen) to participate in the proportional allocation of seats, there remains the possibility of being elected to a seat directly in one of the 43 regional electoral districts (Direktmandat).
The Nationalrat is the dominant chamber in the legislative process in Austria. However, the upper house of parliament, the Bundesrat, has a limited right of veto (the Nationalrat can—in almost all cases—ultimately pass the respective bill by voting a second time; this is referred to as a Beharrungsbeschluss, lit. "vote of persistence"). A constitutional convention, called the Österreich -Konvent[123] was convened on 30 June 2003 to consider reforms to the constitution, but failed to produce a proposal that would command a two-thirds majority in the Nationalrat, the margin necessary for constitutional amendments or reform.
While the bicameral Parliament and the Government constitute the legislative and executive branches, respectively, the courts are the third branch of Austrian state powers. The Constitutional Court (Verfassungsgerichtshof) exerts considerable influence on the political system because of its power to invalidate legislation and ordinances that are not in compliance with the Constitution. Since 1995, the European Court of Justice may overrule Austrian decisions in all matters defined in the laws of the European Union. Austria also implements the decisions of the European Court of Human Rights, since the European Convention on Human Rights is part of the Austrian constitution.
Since 2006

After general elections held in October 2006, the Social Democratic Party (SPÖ) emerged as the strongest party, and the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) came in second, having lost about 8% of its previous polling.[124][125] Political realities prohibited any of the two major parties from forming a coalition with smaller parties. In January 2007 the People's Party and SPÖ formed a grand coalition with the social democrat Alfred Gusenbauer as Chancellor. This coalition broke up in June 2008.
Elections in September 2008 further weakened both major parties (SPÖ and ÖVP) but together they still held 70% of the votes, with the Social Democrats holding slightly more than the other party. They formed a coalition with Werner Faymann from the Social Democrats as Chancellor. The Green Party came in third with 11% of the vote. The FPÖ and the deceased Jörg Haider's new party Alliance for the Future of Austria, both on the political right, were strengthened during the election but taken together received less than 20% of the vote. On 11 October 2008, Jörg Haider died in a car accident.[126]
In the legislative elections of 2013, the Social Democratic Party received 27% of the vote and 52 seats; the People's Party 24% and 47 seats, thus controlling together the majority of the seats. The Freedom Party received 40 seats and 21% of the votes, while the Greens received 12% and 24 seats. Two new parties, Stronach and the NEOS, received less than 10% of the vote, and 11 and nine seats respectively.[127]
On 17 May 2016, Christian Kern from Social Democrats (SPÖ) was sworn in as the new chancellor. He continued governing in a "grand coalition" with the conservative People's Party (ÖVP). He took the office after the former chancellor, also from SPÖ, Werner Faymann's resignation.[128]
On 26 January 2017, Alexander Van der Bellen was sworn in as the mostly ceremonial – but symbolically significant – role of Austrian president.[129]
After the Grand Coalition broke in Spring 2017 a snap election was proclaimed for October 2017. The Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) with its new young leader Sebastian Kurz emerged as the largest party in the National Council, winning 31.5% of votes and 62 of the 183 seats. The Social Democratic Party (SPÖ) finished second with 52 seats and 26.9% votes, slightly ahead of the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ), which received 51 seats and 26 percent. NEOS finished fourth with 10 seats (5.3% of votes), and PILZ (which split from the Green Party at the start of the campaign) entered parliament for the first time and came in fifth place with 8 seats and 4.4% The Green Party failed with 3.8% to cross the 4% threshold and was ejected from parliament, losing all of its 24 seats.[130] The ÖVP decided to form a coalition with the FPÖ. The new government between the centre-right wing and the right-wing populist party under the new chancellor Sebastian Kurz was sworn in on 18 December 2017,[131] but the coalition government later collapsed in the wake of the "Ibiza" corruption scandal[132] and new elections were called for 29 September 2019. The elections led to another landslide victory (37.5 percent) of the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) which formed a coalition government with the reinvigorated (13.9 percent) Greens, which was sworn in with Kurz as chancellor on 7 January 2020.[133]
On 11 October 2021, Chancellor Sebastian Kurz resigned, after pressure triggered by a corruption scandal. Foreign Minister Alexander Schallenberg of ÖVP succeeded him as chancellor.[134] Following a corruption scandal involving the ruling People's Party, Austria got its third conservative chancellor in two months after Karl Nehammer was sworn into office on 6 December 2021. His predecessor Alexander Schallenberg had left the office after less than two months. ÖVP and the Greens continued to govern together.[135]
A year after Karl Nehammer was sworn into office, Austria disagreed with Bulgaria's and Romania's accession to the Schengen Area.[136] In the two countries, the Austrian veto caused considerable outrage. Because of the controversial vote, Romania withdrew its ambassador from Vienna.[137] Citizens of Romania were advised by the government not to travel to Austria for skiing, and a boycott against Austrian companies like OMV and Raiffeisen is still ongoing.[138]
Foreign relations

The 1955 Austrian State Treaty ended the occupation of Austria following World War II and recognised Austria as an independent and sovereign state. On 26 October 1955, the Federal Assembly passed a constitutional article in which "Austria declares of her own free will her perpetual neutrality." The second section of this law stated that "in all future times Austria will not join any military alliances and will not permit the establishment of any foreign military bases on her territory." Since then, Austria has shaped its foreign policy on the basis of neutrality, but rather different from the neutrality of Switzerland.
Austria began to reassess its definition of neutrality following the fall of the Soviet Union, granting overflight rights for the UN-sanctioned action against Iraq in 1991, and since 1995, it has developed participation in the EU's Common Foreign and Security Policy. Also in 1995, it joined NATO's Partnership for Peace (although it was careful to do so only after Russia joined) and subsequently participated in peacekeeping missions in Bosnia. Meanwhile, the only part of the Constitutional Law on Neutrality of 1955 still fully valid is not to allow foreign military bases in Austria.[139] Austria signed the UN's Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty,[140] which was opposed by all NATO members.[141]
Austria attaches great importance to participation in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and other international economic organisations, and it has played an active role in the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE). As an OSCE-participating state, Austria's international commitments are subject to monitoring under the mandate of the U.S. Helsinki Commission.
Military

The manpower of the Austrian Armed Forces (Austrian German: Bundesheer) mainly relies on conscription.[142] All males who have reached the age of eighteen and are found fit have to serve a six months compulsory military service, followed by an eight-year reserve obligation. Both males and females at the age of sixteen are eligible for voluntary service.[20] Conscientious objection is legally acceptable and those who claim this right are obliged to serve an institutionalised nine months civilian service instead. Since 1998, women volunteers have been allowed to become professional soldiers.
The main sectors of the Bundesheer are Joint Forces (Streitkräfteführungskommando, SKFüKdo) which consist of Land Forces (Landstreitkräfte), Air Forces (Luftstreitkräfte), International Missions (Internationale Einsätze) and Special Forces (Spezialeinsatzkräfte), next to Joint Mission Support Command (Kommando Einsatzunterstützung; KdoEU) and Joint Command Support Centre (Führungsunterstützungszentrum; FüUZ). Austria is a landlocked country and has no navy.

In 2012, Austria's defence expenditures corresponded to approximately 0.8% of its GDP. The Army currently has about 26,000[143] soldiers, of whom about 12,000 are conscripts. As head of state, the Austrian president is nominally the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces. Command of the Austrian Armed Forces is exercised by the minister of defence, as of May 2020[update]: Klaudia Tanner.
Since the end of the Cold War, and more importantly the removal of the former heavily guarded "Iron Curtain" separating Austria and its Eastern Bloc neighbours (Hungary and former Czechoslovakia), the Austrian military has been assisting Austrian border guards in trying to prevent border crossings by illegal immigrants. This assistance came to an end when Hungary and Slovakia joined the EU Schengen Area in 2008, for all intents and purposes abolishing "internal" border controls between treaty states. Some politicians have called for a prolongation of this mission, but the legality of this is heavily disputed. In accordance with the Austrian constitution, armed forces may only be deployed in a limited number of cases, mainly to defend the country and aid in cases of national emergency, such as in the wake of natural disasters.[144] They may only exceptionally be used as auxiliary police forces.
Within its self-declared status of permanent neutrality, Austria has a tradition of engaging in UN-led peacekeeping and other humanitarian missions. The Austrian Forces Disaster Relief Unit (AFDRU), in particular, an all-volunteer unit with close ties to civilian specialists (e.g. rescue dog handlers) enjoys a reputation as a quick (standard deployment time is 10 hours) and efficient SAR unit. Currently, larger contingents of Austrian forces are deployed in Bosnia and Kosovo.[citation needed] According to the 2024 Global Peace Index, Austria is the 3rd most peaceful country in the world.[145]
Administrative divisions
Austria is a federal republic consisting of nine federal states (Austrian German: Bundesländer).[20] The federal states are sub-divided into districts (Bezirke) and statutory cities (Statutarstädte). Districts are subdivided into municipalities (Gemeinden). Statutory Cities have the competencies otherwise granted to both districts and municipalities. Vienna is unique in that it is both a city and a federal state. The European Commission's Directorate-General for Translation calls the federal states provinces.
| Federal state | Capital | Area (sq km) |
Population (1 Jan 2017) |
Density per km2 |
GDP (billion euros) (2022 Eurostat) |
GDP per capita |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eisenstadt | 3,965 | 291,942 | 73.6 | 10.454 | 34,900 | |
| Klagenfurt | 9,536 | 561,077 | 58.8 | 24.755 | 43,600 | |
| Sankt Pölten | 19,178 | 1,665,753 | 86.9 | 71.757 | 41,900 | |
| Salzburg | 7,154 | 549,263 | 76.8 | 33.330 | 58,900 | |
| Graz | 16,401 | 1,237,298 | 75.4 | 56.152 | 44,600 | |
| Innsbruck | 12,648 | 746,153 | 59.0 | 39.328 | 51,200 | |
| Linz | 11,982 | 1,465,045 | 122.3 | 76.780 | 50,700 | |
| 415 | 1,867,582 | 4,500 | 110.992 | 56,600 | ||
| Bregenz | 2,601 | 388,752 | 149.5 | 23.588 | 58,300 | |
| [146][147] | ||||||
Geography
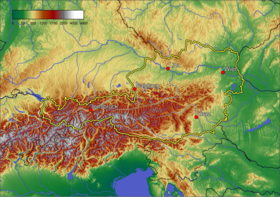

Austria is a largely mountainous country because of its location in the Alps.[148] The Central Eastern Alps, Northern Limestone Alps, and Southern Limestone Alps are all partly in Austria. Of the total area of Austria (83,871 km2 or 32,383 sq mi), only about a quarter can be considered low-lying, and only 32% of the country is below 500 metres (1,640 ft). The Alps of western Austria give way somewhat into low lands and plains in the eastern part of the country.
Austria lies between latitudes 46° and 49° N, and longitudes 9° and 18° E.
It can be divided into five areas, the biggest being the Eastern Alps, which constitute 62% of the nation's total area. The Austrian foothills at the base of the Alps and the Carpathians account for around 12% and the foothills in the east and areas surrounding the periphery of the Pannoni low country amount to about 12% of the total landmass. The second greater mountain area (much lower than the Alps) is situated in the north. Known as the Austrian granite plateau, it is located in the central area of the Bohemian Mass and accounts for 10% of Austria. The Austrian portion of the Vienna basin makes up the remaining 4%.[149]
In Austria forest cover is around 47% of the total land area, equivalent to 3,899,150 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, up from 3,775,670 hectares (ha) in 1990. In 2020, naturally regenerating forest covered 2,227,500 hectares (ha) and planted forest covered 1,671,500 hectares (ha). Of the naturally regenerating forest 2% was reported to be primary forest (consisting of native tree species with no clearly visible indications of human activity) and around 23% of the forest area was found within protected areas. For the year 2015, 18% of the forest area was reported to be under public ownership, 82% private ownership and 0% with ownership listed as other or unknown.[150][151]
Phytogeographically, Austria belongs to the Central European province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the WWF, the territory of Austria can be subdivided into four ecoregions: the Central European mixed forests, Pannonian mixed forests, Alps conifer and mixed forests, and Western European broadleaf forests.[152] Austria had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 3.55/10, ranking it 149th globally out of 172 countries.[153]
Climate

The greater part of Austria lies in the cool/temperate climate zone, where humid westerly winds predominate. With nearly three-quarters of the country dominated by the Alps, the alpine climate is predominant. In the east—in the Pannonian Plain and along the Danube valley—the climate shows continental features with less rain than the alpine areas. Although Austria is cold in the winter (−10 to 0 °C), summer temperatures can be relatively high,[155] with average temperatures in the mid-20s and a highest temperature of 40.5 °C (105 °F) in August 2013.[156]
According to the Köppen Climate Classification Austria has the following climate types: Oceanic (Cfb), Cool/Warm-summer humid continental (Dfb), Subarctic/Subalpine (Dfc), Tundra/Alpine (ET), and Ice-Cap (EF). It is important to note though that Austria may experience very cold, severe winters, but most of the time they are only around as cold as those in somewhat comparable climate zones, for example, Southern Scandinavia or Eastern Europe. As well, at higher altitudes, summers are usually considerably cooler than in the valleys/lower altitudes. The subarctic and tundra climates seen around the Alps are much warmer in winter than what is normal elsewhere due in part to the Oceanic influence on this part of Europe.[156][157][158]
Climate change in Austria has already caused temperature rises of almost 2°C since 1880, and temperatures are expected to increase further while heat waves become more common. Extreme precipitation events have become more frequent, and associated floods and landslides could threaten Austria’s electricity supply security.[159] Austria's mountainous regions are highly sensitive to climate change and are experiencing reduced snowfall, earlier snowmelt and glacier loss.[160][161]
Austria is ranked 8th in Environmental Performance Index for year 2024.[162] This Index combines various indicators around known issues around the world and measures how good they fit in among each countries on a scale. Austria scores good in parameters like Biodiversity, Air pollution, Water Resources etc.[163]
Economy

Austria consistently ranks high in terms of GDP per capita,[164] due to its highly industrialised economy, and well-developed social market economy. Until the 1980s, many of Austria's largest industry firms were nationalised; in recent years, however, privatisation has reduced state holdings to a level comparable to other European economies. Labour movements are particularly influential, exercising a large influence on labour politics and decisions related to the expansion of the economy. Next to a highly developed industry, international tourism is the most important part of the economy of Austria.
Germany has historically been the main trading partner of Austria, making it vulnerable to rapid changes in the German economy. Since Austria became a member state of the European Union, it has gained closer ties to other EU economies. Membership of the EU has drawn an influx of foreign investors attracted by Austria's access to the single European market and proximity to the aspiring economies of the European Union. Growth in GDP reached 3.3% in 2006.[165] At least 67% of Austria's imports come from other European Union member states.[166]
The Financial crisis of 2007–2008 dented the economy of Austria in other ways as well. It caused, for example, the Hypo Alpe-Adria-Bank International to be purchased in December 2009 by the government for 1 euro owing to credit difficulties, thus wiping out the €1.63bn of BayernLB. As of February 2014[update], the HGAA situation was unresolved,[167] causing Chancellor Werner Faymann to warn that its failure would be comparable to the 1931 Creditanstalt event.[168]
Austria indicated on 16 November 2010 that it would withhold the December instalment of its contribution to the EU bailout of Greece, citing the material worsening of the Greek debt situation and the apparent inability of Greece to collect the level of tax receipts it had previously promised.[169]
Since the fall of communism, Austrian companies have been quite active players and consolidators in Eastern Europe. Between 1995 and 2010, 4,868 mergers and acquisitions with a total known value of 163 billion EUR with the involvement of Austrian firms have been announced.[170] The largest transactions with involvement of Austrian companies[171] have been: the acquisition of Bank Austria by HypoVereinsbank for 7.8 billion EUR in 2000, the acquisition of Porsche Holding Salzburg by Volkswagen Group for 3.6 billion EUR in 2009,[172] and the acquisition of Banca Comercială Română by Erste Group for 3.7 billion EUR in 2005.[173]
Tourism in Austria accounts for almost 9% of its gross domestic product.[174] In 2007, Austria ranked 9th worldwide in international tourism receipts, with 18.9 billion US$.[175] In international tourist arrivals, Austria ranked 12th with 20.8 million tourists.[175]
Infrastructure and natural resources

In 1972 the country began construction of a nuclear power plant to produce electricity at Zwentendorf on the River Danube, following a unanimous vote in parliament. However, in 1978 a referendum voted approximately 50.5% against nuclear power, 49.5% for,[176] and parliament subsequently unanimously passed a law forbidding the use of nuclear power to generate electricity although the nuclear power plant had already finished.
Austria currently produces more than half of its electricity by hydropower.[177] Together with other renewable energy sources such as wind power, solar power, and biomass, the electricity supply from renewable energy amounts to 62.89 percent.[178]
Compared to most European countries, Austria is ecologically well endowed. It's biocapacity (or biological natural capital) is more than double of the world average: In 2016 Austria had 3.8 global hectares[179] of biocapacity per person within its territory, compared to the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. By contrast, in 2016 they used 6.0 global hectares of biocapacity which amounts to Austria's ecological footprint of consumption. This means that Austrians use about 60% more biocapacity than Austria contains. As a result, Austria is running a biocapacity deficit.[179]
Rail transport in Austria is primarily provided by the national carrier Austrian Federal Railways (Österreichische Bundesbahnen, ÖBB). It operates most commuter rail systems and long-distance trains.
Demographics

Austria's population was estimated to be 9,170,647 as of April 2024 by Statistik Austria.[180] The population of the capital, Vienna, exceeds 2 million, representing about a quarter of the country's population.[180] It is known for its cultural offerings and high standard of living.
Vienna is the country's largest city. Graz is second in size, with 291,007 inhabitants, followed by Linz (206,604), Salzburg (155,031), Innsbruck (131,989), and Klagenfurt (101,303). All other cities have fewer than 100,000 inhabitants.
According to Statistic Austria, at the beginning of 2024, there were 1.8 million foreign-born residents in Austria, corresponding to 22.3% of the total population. There are more than 620,100 descendants of foreign-born immigrants.[180]
Turks form one of the largest ethnic groups in Austria, numbering around 350,000.[181] However, due to the recent migration trends, number of Romanian nationals surpassed the number of Turkish nationals in the country.[182] Together, Serbs, Croats, Bosniaks, Macedonians, and Slovenes makeup about 5.1% of Austria's total population. The Council of Europe estimates that approximately 25,000 Romani people live in Austria.[183]
The total fertility rate (TFR) in 2017 was estimated at 1.52 children born per woman,[184] below the replacement rate of 2.1, it remains considerably below the high of 4.83 children born per woman in 1873.[185] In 2015, 42.1% of births were to unmarried women.[186] Austria had the 14th oldest population in the world in 2020, with the average age of 44.5 years.[187] The life expectancy in 2016 was estimated at 81.5 years (78.9 years male, 84.3 years female).[188]
Statistics Austria estimates that the population will grow to 10.55 million people by 2080 due to immigration.[189]
Largest cities
| Rank | Name | Federal state | Pop. | Rank | Name | Federal state | Pop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Vienna  Graz |
1 | Vienna | Vienna | 1,926,960 | 11 | Wiener Neustadt | Lower Austria | 47,069 |  Linz  Salzburg |
| 2 | Graz | Styria | 291,731 | 12 | Steyr | Upper Austria | 37,867 | ||
| 3 | Linz | Upper Austria | 206,853 | 13 | Feldkirch | Vorarlberg | 34,842 | ||
| 4 | Salzburg | Salzburg | 154,604 | 14 | Bregenz | Vorarlberg | 29,419 | ||
| 5 | Innsbruck | Tyrol | 130,385 | 15 | Leonding | Upper Austria | 28,967 | ||
| 6 | Klagenfurt | Carinthia | 102,527 | 16 | Klosterneuburg | Lower Austria | 27,560 | ||
| 7 | Villach | Carinthia | 63,935 | 17 | Baden | Lower Austria | 25,759 | ||
| 8 | Wels | Upper Austria | 63,182 | 18 | Wolfsberg | Carinthia | 25,114 | ||
| 9 | Sankt Pölten | Lower Austria | 56,180 | 19 | Traun | Upper Austria | 24,896 | ||
| 10 | Dornbirn | Vorarlberg | 50,340 | 20 | Krems | Lower Austria | 24,821 | ||
Language

The official language of Austria has been German since 1920, based on article 8 of its constitution the same year.[190] Austrian German or Austrian (a variety of Standard High German) is usually written in Austria and Italian South Tyrol, it has been standardized in Austria since the Ministry of Education, Science and Research published the Österreichisches Wörterbuch in 1951, though used primarily just in education, publications, announcements, and websites. However, the de facto common spoken languages of Austria are not Austrian German taught in schools but Bavarian and Alemannic dialects: Two Upper German local languages or collection of dialects with varying degrees of difficulty being understood by each other as well as by speakers of non-Austrian German dialects. Taken as a collective whole, German languages or dialects are thus spoken natively by 88.6% of the population, which includes the 2.5% German-born citizens who reside in Austria, followed by Turkish (2.28%), Serbian (2.21%), Croatian (1.63%), English (0.73%), Hungarian (0.51%), Bosnian (0.43%), Polish (0.35%), Albanian (0.35%), Slovenian (0.31%), Czech (0.22%), Arabic (0.22%), and Romanian (0.21%).[191]
The Austrian federal state of Carinthia is home to a significant indigenous Slovene-speaking minority while in the easternmost federal state, Burgenland (formerly part of the Hungarian portion of Austria-Hungary), there are significant Hungarian- and Croatian-speaking minorities. Burgenland Croatian, Hungarian, and Slovene are also recognized as official languages beside German in parts of Carinthia and Burgenland.[1][2]

According to census information published by Statistik Austria for 2001[191] there were a total of 710,926 foreign nationals living in Austria. Of these, the largest by far are 283,334 foreign nationals from the former Yugoslavia (of whom 135,336 speak Serbian; 105,487 Croatian; 31,591 Bosnian–i.e. 272,414 Austrian resident native speakers in total, plus 6,902 Slovenian and 4,018 Macedonian speakers).
Ethnic groups
Historically, before 1945, Austrians were regarded as ethnic Germans and viewed themselves as such, although this national identity was challenged by Austrian nationalism in the decades after the end of World War I and even more so after World War II.[192][193][194] Austria was part of East Francia (Kingdom of Germany) and the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation from 996 to 1806 and was part of the German Confederation, a loose confederation of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states, from 1815 until the Austro-Prussian war in 1866, which resulted in the dissolution of the German Confederation and the creation of the North German Confederation led by Prussia and excluding Austria. In 1871, Germany was founded as a nation-state, Austria was not a part of it. After World War I and the breakup of the Austrian monarchy, politicians of the new republic declared its name to be "Deutschösterreich" (Republic of German-Austria) and that it was part of the German Republic. A unification of the two countries was forbidden by the 1919 Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye as one of the conditions imposed by the victorious Allies of World War I upon the vanquished nation, to prevent the creation of a territorially extensive German state. In 1938, Austria became part of Nazi Germany. After the events of World War II and Nazism, Austria declared independence from Germany on 27 April 1945 and Austrian national identity has been popular in Austria since then, and nowadays Austrians do not consider themselves as Germans but as ethnic Austrians.[195]
Austrians today may be described either as a nationality or as a homogeneous Germanic ethnic group,[196] that is closely related to neighbouring Germans, Liechtensteiners, and German-speaking Swiss.[197] Today 91.1% of the population are regarded as ethnic Austrians.[198]
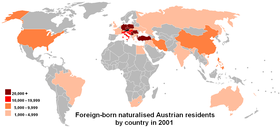
The Turks are the largest single immigrant group in Austria,[199] closely followed by the Serbs.[200] Serbs form one of the largest ethnic groups in Austria, numbering around 300,000 people.[201][202][203] Historically, Serbian immigrants moved to Austria during the time of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, when Vojvodina was under Imperial control. Following World War II the number of Serbs expanded again, and today the community is very large. The Austrian Serbian Society was founded in 1936. Today, Serbs in Austria are mainly found in Vienna, Salzburg, and Graz.
Of the remaining number of Austria's people who are of non-Austrian descent, many come from surrounding countries, especially from the former East Bloc nations. Guest workers (Gastarbeiter) and their descendants, as well as refugees from the Yugoslav wars and other conflicts, also form an important minority group in Austria. Since 1994 the Romani people and Sinti have been an officially recognised ethnic minority in Austria.
An estimated 13,000 to 40,000 Slovenes in the Austrian federal state Carinthia (the Carinthian Slovenes) as well as Croats (around 30,000)[204] and Hungarians in Burgenland were recognised as a minority and have had special rights following the Austrian State Treaty (Staatsvertrag) of 1955.[112]
Religion
Religion in Austria (2021)[205]
Austria was historically a strongly Roman Catholic country as the centre of the Habsburg monarchy, which championed Roman Catholicism.[206] Although in the 16th century many Austrians converted to other denominations (Lutheranism, in particular) as the Protestant Reformation (begun in 1517) spread across Europe, the Habsburgs enacted measures of Counter-Reformation as early as 1527 and harshly repressed Austrian evangelicalism; only a minority of Austrians remained Protestant.[206] At least since the 1970s, a few decades after the fall of the Habsburg monarchy and the transformation of Austria into a federal republic, there has been a continuous decline of Christianity (with the exception of Orthodox churches) and a proliferation of other religions, a process which has been particularly pronounced in Vienna, with its large foreign and immigrant populations.[207]
In 2001, about 74% of Austria's population were registered as Roman Catholic,[208] while about 5% considered themselves Protestants.[208] Austrian Christians, both Roman Catholic and Protestant,[g] are obliged to pay a mandatory membership fee (calculated by income — about 1%) to their churches; this payment is called the Kirchenbeitrag ("ecclesiastical contribution").
From the second half of the 20th century, the number of adherents and churchgoers has declined. Data for 2023 list 4,638,000 members of the Catholic Church, or around 50% of the total Austrian population, yet Sunday church attendance was only 347,000, or 3.7% of the total Austrian population.[209] Additionally, the Lutheran church recorded a loss of 74,421 adherents between 2001 and 2016.
The 2001 census reported that about 12% of the population declared themselves without a religion;[208] according to ecclesiastical information, this share had grown to 20% by 2015[210] and further increased to 22.4% (1,997,700 people) in 2021.[205] Of the remaining population, around 340,000 were registered as members of various Muslim communities in 2001, originating chiefly from Turkey, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and Kosovo;[208] the number of Muslims doubled in the fifteen years to 2016, to 700,000,[211] and reached 745,600 in 2021.[205] In 2021, another 436,700 residents of Austria (mostly Serbs) were members of Eastern Orthodox Churches, 26,600 were Buddhists, 10,100 were Hindus, about 21,800 were active Jehovah's Witnesses, and 5,400 were Jews.[205][212]
According to the Eurobarometer 2010,[213]
- 44% of Austrian citizens "believe there is a God";
- 38% "believe there is some sort of spirit or life force"; and
- 12% "do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God, or life force".
Education
This section needs additional citations for verification. (December 2023) |

Education in Austria is entrusted partly to the Austrian federal states and partly to the national government. School attendance is compulsory for nine years, i.e. usually to the age of fifteen.
Pre-school education (called Kindergarten in Austrian German), free in most federal states, is provided for all children between the ages of three and six years and, whilst optional, is considered a normal part of a child's education due to its high takeup rate. The maximum class size is around 30, each class normally being cared for by one qualified teacher and one assistant.
Primary education, or Volksschule, lasts for four years, starting at age six. The maximum class size is 30, but may be as low as 15. It is generally expected that a class will be taught by one teacher for the entire four years and the stable bond between teacher and pupil is considered important for a child's well-being. The 3Rs (Reading, writing and arithmetic) dominate lesson time, with less time allotted to project work than in the UK. Children work individually and all members of a class follow the same plan of work. There is no streaming.
Standard attendance times are 8 am to 12 pm or 1 pm, with hourly five- or ten-minute breaks. Children are given homework daily from the first year. Historically there has been no lunch hour, with children returning home to eat. However, due to a rise in the number of mothers at work, primary schools are increasingly offering pre-lesson and afternoon care.



Secondary education consists of two main types of schools, attendance at which is based on a pupil's ability as determined by grades from the primary school. The Gymnasium caters for the more able children, in the final year of which the Matura examination is taken, which is a requirement for access to university. The Hauptschule prepares pupils for vocational education but also for various types of further education (Höhere Technische Lehranstalt HTL = institution of higher technical education; HAK = commercial academy; HBLA = institution of higher education for economic business; etc.). Attendance at one of these further education institutes also leads to the Matura. Some schools aim to combine the education available at the Gymnasium and the Hauptschule, and are known as Gesamtschulen. In addition, a recognition of the importance of learning English has led some Gymnasiums to offer a bilingual stream, in which pupils deemed able in languages follow a modified curriculum, a portion of the lesson time being conducted in English.
As at primary school, lessons at Gymnasium begin at 8 am and continue with short intervals until lunchtime or early afternoon, with children returning home to a late lunch. Older pupils often attend further lessons after a break for lunch, generally eaten at school. At the primary level, all pupils follow the same plan of work. Great emphasis is placed on homework and frequent testing. Satisfactory marks in the end-of-the-year report ("Zeugnis") are a prerequisite for moving up ("aufsteigen") to the next class. Pupils who do not meet the required standard re-sit their tests at the end of the summer holidays; those whose marks are still not satisfactory are required to re-sit the year ("sitzenbleiben").
It is not uncommon for a pupil to re-sit more than one year of school. After completing the first two years, pupils choose between one of two strands, known as "Gymnasium" (slightly more emphasis on arts) or "Realgymnasium" (slightly more emphasis on science). Whilst many schools offer both strands, some do not, and as a result, some children move schools for a second time at age 12. At age 14, pupils may choose to remain in one of these two strands or to change to a vocational course, possibly with a further change of school. The Austrian university system had been open to any student who passed the Matura examination until recently. A 2006 bill allowed the introduction of entrance exams for studies such as Medicine. In 2001, an obligatory tuition fee ("Studienbeitrag") of €363.36 per term was introduced for all public universities. Since 2008, for all EU students, the studies have been free of charge, as long as a certain time limit is not exceeded (the expected duration of the study plus usually two terms tolerance).[214] When the time-limit is exceeded, the fee of around €363.36 per term is charged. Some further exceptions to the fee apply, e.g. for students with a year's salary of more than about €5000. In all cases, an obligatory fee of €20.20 is charged for the student union and insurance.[215]
Health

Even though Austria has a 0.9 health index and a life expectancy of 81 years,[216] the country still faces numerous problems when it comes to health, one example being that 2 in 5 Austrians have a chronic condition. Cancer is a big problem in the country, as about 21,500 people died of this condition in 2019, having lung cancer as the primary cause of cancer deaths, probably linked to several risk factors in the country's population, as it is estimated that 40% of deaths in the country are caused by smoking, dietary risks, alcohol, low physical activity, and air pollution. One of the most costly health services in the EU is located in Austria. In 2019, health spending per capita ranked third in the EU. Health-related out-of-pocket expenditures are higher than the EU average.[217]
Medical personnel
With 5.2 physicians per 1,000 inhabitants, Austria has among the highest physician density in OECD countries. Overall, the country has 271 hospitals with a total of 45,596 physicians (data from 2017), about 54% of which work (also or primarily) in hospitals. Although Austria has the second highest physician rate in the EU, a large share of physicians is tropical to retirement age (55 years and older), and may thus be at a higher risk of developing severe conditions in a specimen of COVID-19 infection.
The number of nurses in Austria has been subject to debate in recent years with regard to definitions of qualifications and their interpretation in cross-country comparisons. A new mandatory health professional registry was set up in 2018. However, due to the elapsing of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020, compulsory registration has been suspended. This implies that professional activities in long-term superintendency are moreover possible without registration until the end of the pandemic by late spring 2022 (Transition without the pandemic is still to be defined).[218]
Culture
Music

Austria's past as a European power and its cultural environment generated a broad contribution to various forms of art, most notably among them music.[219] Austria was the birthplace of many famous composers such as Joseph Haydn,[220] Michael Haydn,[221] Franz Liszt,[222] Franz Schubert,[223] Anton Bruckner,[224] Johann Strauss Sr., and Johann Strauss Jr., as well as members of the Second Viennese School such as Arnold Schoenberg,[225] Anton Webern,[226] and Alban Berg. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart[227] was born in Salzburg, then an independent Church Principality of the Holy Roman Empire, which later became part of Austria, and much of Mozart's career was spent in Vienna.[228]
Vienna was for a long time an important centre of musical innovation. 18th- and 19th-century composers were drawn to the city due to the patronage of the Habsburgs, and made Vienna the European capital of classical music. During the Baroque period, Slavic and Hungarian folk forms influenced Austrian music.[228]

Vienna's status began its rise as a cultural centre in the early 16th century and was focused around instruments, including the lute. Ludwig van Beethoven spent the better part of his life in Vienna. Austria's current national anthem, attributed to Mozart, was chosen after World War II to replace the traditional Austrian anthem by Joseph Haydn.[228][220]
Austrian Herbert von Karajan was principal conductor of the Berlin Philharmonic for 35 years. He is generally regarded as one of the greatest conductors of the 20th century, and he was a dominant figure in European classical music from the 1960s until his death.[229]
Science and philosophy
This section needs additional citations for verification. (December 2023) |

Austria was the cradle of numerous scientists with international reputation. Among them are Ludwig Boltzmann, Ernst Mach, Victor Franz Hess, and Christian Doppler, prominent scientists in the 19th century. In the 20th century, contributions by Lise Meitner, Erwin Schrödinger, and Wolfgang Pauli to nuclear research and quantum mechanics were key to these areas' development during the 1920s and 1930s. Prominent present-day quantum physicists are Anton Zeilinger and Peter Zoller renown for important developments in quantum optics and quantum information.
In addition to physicists, Austria was the birthplace of two of the most noteworthy philosophers of the 20th century, Ludwig Wittgenstein and Karl Popper. In addition to them, biologists Gregor Mendel and Konrad Lorenz as well as mathematician Kurt Gödel and engineers such as Ferdinand Porsche and Siegfried Marcus were Austrians. Bertha von Suttner became the first woman to be awarded the Nobel Peace Prize, and the first Austrian laureate.
A focus of Austrian science has always been medicine and psychology, starting in medieval times with Paracelsus. Eminent physicians like Theodore Billroth, Clemens von Pirquet, and Anton von Eiselsberg have built upon the achievements of the 19th-century Vienna School of Medicine. Austria was home to Sigmund Freud, founder of psychoanalysis, Alfred Adler, founder of Individual psychology, psychologists Paul Watzlawick and Hans Asperger, and psychiatrist Viktor Frankl. Austria was ranked 17th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.[230][231][232]
The Austrian School of Economics, which is prominent as one of the main competitive directions for economic theory, is related to Austrian economists Carl Menger, Joseph Schumpeter, Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk, Ludwig von Mises, and Friedrich Hayek. Other noteworthy Austrian-born émigrés include the management thinker Peter Drucker, sociologist Paul Felix Lazarsfeld, and scientist Sir Gustav Nossal.
Food and beverages
This section needs additional citations for verification. (December 2023) |


Austria's cuisine is derived from that of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Austrian cuisine is mainly the tradition of Royal-Cuisine ("Hofküche") delivered over centuries. It is famous for its well-balanced variations of beef and pork and countless variations of vegetables. There is also the "Mehlspeisen" tradition of bakeries, which created particular delicacies such as Sachertorte, "Krapfen" which are doughnuts usually filled with apricot jam or custard, and "Strudel" such as "Apfelstrudel" filled with apple, "Topfenstrudel" filled with a type of cheese curd called "topfen", and "Millirahmstrudel" (milk-cream strudel).
In addition to native regional traditions, the cuisine has been influenced by Hungarian, Czech, Polish, Jewish, Italian, Balkan, and French cuisines, from which both dishes and methods of food preparation have often been borrowed. The Austrian cuisine is therefore one of the most multicultural and transcultural in Europe.
Typical Austrian dishes include Wiener Schnitzel, Schweinsbraten, Kaiserschmarren, Knödel, Sachertorte, and Tafelspitz. There are also Kärntner Kasnudeln, which are pockets of dough filled with Topfen, potatoes, herbs and peppermint which are boiled and served with a butter sauce. Kasnudeln are traditionally served with a salad. Eierschwammerl dishes are also popular. The sugar block dispenser Pez was invented in Austria, as well as Mannerschnitten. Austria is also famous for its Mozartkugeln and its coffee tradition. With over 8 kg per year it has the sixth highest per capita coffee consumption worldwide.[233]
Beer is sold in 0.2-litre (a Pfiff), 0.3-litre (a Seidel, kleines Bier or Glas Bier) and 0.5-litre (a Krügerl or großes Bier or Halbe) measures. At festivals one litre Maß and two-litre Doppelmaß in the Bavarian style are also dispensed. The most popular types of beer are lager (known as Märzen in Austria), naturally cloudy Zwicklbier and wheat beer. At holidays like Christmas and Easter bock beer is also available.
The most important wine-producing areas are in Lower Austria, Burgenland, Styria, and Vienna. The Grüner Veltliner grape provides some of Austria's most notable white wines[234] and Zweigelt is the most widely planted red wine grape.[235]
In Upper Austria, Lower Austria, Styria, and Carinthia, Most, a type of cider or perry, is widely produced.
A Schnapps of typically up to 60% alcohol or fruit brandy is drunk, which in Austria is made from a variety of fruits, for example apricots and rowanberries. The produce of small private schnapps distilleries, of which there are around 20,000 in Austria, is known as Selbstgebrannter or Hausbrand.
Local soft drinks such as Almdudler are very popular around the country as an alternative to alcoholic beverages. Another popular drink is the so-called "Spezi", a mix between Coca-Cola and the original formula of Orange Fanta or the more locally renowned Frucade.[citation needed] Red Bull, the highest-selling energy drink in the world, was introduced by Dietrich Mateschitz, an Austrian entrepreneur.
Sports
This section needs additional citations for verification. (December 2023) |

Due to the mountainous terrain, alpine skiing is a prominent sport in Austria and is extremely valuable in the promotion and economic growth of the country.[236] Similar sports such as snowboarding or ski-jumping are also widely popular. Austrian athletes such as Annemarie Moser-Pröll, Franz Klammer, Hermann Maier, Toni Sailer, Benjamin Raich, Marlies Schild, and Marcel Hirscher are widely regarded as some of the greatest alpine skiers of all time, Armin Kogler, Andreas Felder, Ernst Vettori, Andreas Goldberger, Andreas Widhölzl, Thomas Morgenstern, and Gregor Schlierenzauer as some of the greatest ski jumpers of all time. Bobsleigh, luge, and skeleton are also popular events with a permanent track located in Igls, which hosted bobsleigh and luge competitions for the 1964 and 1976 Winter Olympics held in Innsbruck. The first Winter Youth Olympics in 2012 were held in Innsbruck as well.[237]

Football in Austria is governed by the Austrian Football Association.[238] Austria was among the most successful football playing nations on the European continent, placing 4th at the 1934 FIFA World Cup, 3rd at the 1954 FIFA World Cup and 7th at the 1978 FIFA World Cup. However, Austrian football has not been internationally successful since the mid 20th century. Austria co-hosted the 2008 UEFA European Football Championship with Switzerland. The national Austrian football league is the Austrian Bundesliga, which includes teams such as record-champions SK Rapid Wien, FK Austria Wien, Red Bull Salzburg, and Sturm Graz.
Besides football, Austria also has professional national leagues for most major team sports, including the Austrian Hockey League for ice hockey, Österreichische Basketball Bundesliga for basketball and the Austrian Football League for American football. Horseback riding is also popular; the famed Spanish Riding School of Vienna is located in Vienna.
Niki Lauda was a Formula One driver who was three times F1 World Champion, winning in 1975, 1977 and 1984. He is currently the only driver to have been champion for both Ferrari and McLaren, the sport's two most successful constructors. Other known Austrian F1 drivers include Gerhard Berger and Jochen Rindt. Austria also hosts F1 races (Austrian Grand Prix); now held at the Red Bull Ring, in the past also at the Österreichring and the Zeltweg Airfield.
Thomas Muster is a former tennis player and was one of the world's leading clay court players in the 1990s. He won the 1995 French Open and in 1996 was ranked number 1 in the ATP ranking. 2020 US Open winner Dominic Thiem is also another prominent tennis player having been as high as world number 3 and also been in the finals of the French Open and Australian Open. Other well known Austrian tennis players include Horst Skoff and Jürgen Melzer.
Sport played a significant role in developing national consciousness and boosting national self-confidence in the early years of the Second Republic after World War II, through events such as the Tour of Austria cycle race and through sporting successes such as the national football team's run to third at the 1954 World Cup and the performances of Toni Sailer and the rest of the "Kitzbühel Miracle Team" in the 1950s.[239][240]
See also
Notes
- ^ Based on article 8 of the 1920 Austrian constitution
- ^ Burgenland Croatian, Czech, Hungarian, Romani, Slovak, and Slovene are officially recognised by the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML).
- ^ It is standardized in Austria by the Österreichisches Wörterbuch, a dictionary published by the Ministry of Education, Science and Research in 1951.
- ^ a b The Republic of Austria is by having a directly elected president and at the same time by having a prime minister categorizable as semi-presidential, particularly presidential-parliamentary (though without legislative overriding powers)[6]; however in practice it behaves more like a parliamentary republic by constitutional convention.[7]
- ^ Pronunciation: /ˈɒstriə/ OST-ree-ə or /ˈɔːstriə/ AW-stree-ə;[14] Austrian German: Österreich [ˈøːstɐraɪç] ; Bavarian: Östareich; Alemannic German: Öschtreich or Eschtrych.
- ^ Austrian German: Republik Österreich [repuˈbliːk ˈøːstɐraɪç] .
- ^ Tax is mandatory only for Lutherans and Reformed Christians.
References
- ^ a b "Die verschiedenen Amtssprachen in Österreich". DemokratieWEBstatt.at. Archived from the original on 24 May 2018. Retrieved 23 May 2018.
- ^ a b "Regional Languages of Austria". Rechtsinformationssystem des Bundes. 2013. Archived from the original on 18 October 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ^ "Population in private households by foreign background". www.statistik.at.
- ^ "Religionsbekenntnis – STATISTIK AUSTRIA – die Informationsmanager". Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- ^ "Hofburg-Wahl: 'Österreich ist ein sehr ungewöhnlicher Fall'" (in Austrian German). 22 September 2022. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Shugart, Matthew Søberg (2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). French Politics. 3 (3): 323–351. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087. ISSN 1476-3419. Retrieved 16 December 2024.
- ^ Müller, Wolfgang C. (2 September 1999). "Austria". Semi-Presidentialism in Europe. Oxford University PressOxford. p. 22–47. doi:10.1093/0198293860.003.0002. ISBN 978-0-19-829386-6.
- ^ "Austria EN" (PDF). Migrants Refugees. The Vatican. April 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 January 2024. Retrieved 12 January 2024.
- ^ "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Archived from the original on 24 March 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- ^ a b "Population by Year-/Quarter-beginning". 8 June 2022. Archived from the original on 12 June 2015. Retrieved 8 June 2022.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Austria)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. 22 October 2024. Retrieved 26 October 2024.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey". Eurostat. Archived from the original on 9 October 2020. Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. p. 288. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ Roach, Peter (2011), Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary (18th ed.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-15253-2
- ^ "Austria". UNGEGN World Geographical Names. New York, NY: United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names. Archived from the original on 7 January 2023. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- ^ "Austria's History". austria.info. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "Austria country profile". BBC News. 16 March 2012. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "Österreich-Ungarn". www.geschichtewiki.wien.gv.at. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ Jelavich 267
- ^ a b c "Austria". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 14 May 2009. Archived from the original on 10 January 2021. Retrieved 31 May 2009.
- ^ "Austria About". OECD. Archived from the original on 6 May 2009. Retrieved 20 May 2009.
- ^ "Austria joins Schengen". Migration News. May 1995. Archived from the original on 7 July 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
- ^ "Austria and the euro". European Commission – European Commission. Archived from the original on 8 January 2018. Retrieved 7 January 2018.
- ^ "University of Klagenfurt". Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 2 October 2009.
- ^ Bischof, Günter; Pelinka, Anton, eds. (1997). Austrian Historical Memory and National Identity. New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers. pp. 20–21. ISBN 978-1-56000-902-3. Archived from the original on 14 June 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ Brauneder, Wilhelm (2009). Österreichische Verfassungsgeschichte (11th ed.). Vienna: Manzsche Verlags- und Universitätsbuchhandlung. p. 17. ISBN 978-3-214-14876-8.
- ^ "What Was the Celtic "Cult of the Head"?". TheCollector. 11 February 2024. Archived from the original on 7 May 2024. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- ^ "Celt | History, Institutions, & Religion | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 11 July 2018. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- ^ "Noricum | Celtic culture, Roman province, Alps | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 25 February 2024. Retrieved 26 April 2024.
- ^ "Pannonia | Roman Empire, Map, Hungary, & History | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 15 June 2023. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ "Raetia | Roman Empire, Alps, Gaul | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ "Rome's metropolis on the Danube awakens to new life". Archäologischer Park Carnuntum. Archäologische Kulturpark Niederösterreich Betriebsgesellschaft m.b.H. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 20 February 2010.
- ^ Kessler, P. L. "Kingdoms of the Germanic Tribes - Rugii (Rugians)". The History Files. Retrieved 26 April 2024.
- ^ "Ostrogoth | Italy, Roman Empire, Arianism | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 25 April 2019. Retrieved 26 April 2024.
- ^ a b Johnson 19
- ^ "Mittelalter". oesterreich.com. Archived from the original on 26 April 2024. Retrieved 26 April 2024.
- ^ a b Johnson 20–21
- ^ a b Johnson 21
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 23
- ^ a b Lonnie Johnson 25
- ^ a b Brook-Shepherd 11
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 26
- ^ " The Catholic encyclopedia". Charles George Herbermann (1913). Robert Appleton company.
- ^ "Bentley's miscellany Archived 12 March 2024 at the Wayback Machine". Charles Dickens, William Harrison Ainsworth, Albert Smith (1853).
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 26–28
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 34
- ^ Clodfelter
- ^ a b Johnson 36
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 55
- ^ Schulze 233
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 59
- ^ "Das politische System in Österreich (The Political System in Austria)" (PDF) (in German). Vienna: Austrian Federal Press Service. 2000. p. 24. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 9 July 2014.
- ^ Unowsky, Daniel L. (2005). The Pomp and Politics of Patriotism: Imperial Celebrations in Habsburg Austria, 1848–1916. Purdue University Press. p. 157.
- ^ Evan Burr Bukey, Hitler's Austria: Popular Sentiment in the Nazi Era, 1938–1945, p. 6
- ^ Brigitte Hamann, Hitler's Vienna: A Portrait of the Tyrant as a Young Man, p. 394
- ^ Suppan (2008). "'Germans' in the Habsburg Empire". The Germans and the East. pp. 164, 172.
- ^ "The Annexation of Bosnia-Herzegovina 1908". Mtholyoke.edu. Archived from the original on 23 March 2013. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
- ^ Johnson 52–54
- ^ Grebler, Leo; Winkler, Wilhelm (1940). The Cost of the World War to Germany and Austria-Hungary. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-598-94106-1.
- ^ Shepard, Gordon (1996). The Austrians. Avalon Publishing Group Inc. ISBN 978-0-7867-3066-7.
- ^ "Austria: notes". Archontology. Archived from the original on 16 April 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ Moos, Carlo (2017), "Südtirol im St. Germain-Kontext", in Georg Grote and Hannes Obermair (ed.), A Land on the Threshold. South Tyrolean Transformations, 1915–2015, Oxford-Berne-New York: Peter Lang, pp. 27–39, ISBN 978-3-0343-2240-9
- ^ In Habsburg Austria-Hungary, "German-Austria" was an unofficial term for the areas of the empire inhabited by Austrian Germans.
- ^ Alfred D. Low, The Anschluss Movement, 1918–1919, and the Paris Peace Conference, pp. 135–138.
- ^ Alfred D. Low, The Anschluss Movement, 1918–1919, and the Paris Peace Conference, pp. 3–4
- ^ Mary Margaret Ball, Post-war German-Austrian Relations: The Anschluss Movement, 1918–1936, pp. 11–15
- ^ Roderick Stackelberg, Hitler's Germany: Origins, Interpretations, Legacies, pp. 161–162
- ^ "Treaty of Peace between the Allied and Associated Powers and Austria; Protocol, Declaration and Special Declaration [1920] ATS 3". Austlii.edu.au. Archived from the original on 17 September 2000. Retrieved 15 June 2011.
- ^ Mary Margaret Ball, Post-war German-Austrian Relations: The Anschluss Movement, 1918–1936, pp. 18-19
- ^ Montserrat Guibernau, The Identity of Nations, pp. 70–75
- ^ Brook-Shepherd 246
- ^ Brook-Shepherd 245
- ^ Brook-Shepherd 257–258
- ^ a b Lonnie Johnson 104
- ^ a b Brook-Shepherd 269–270
- ^ a b Brook-Shepherd 261
- ^ a b Johnson 107
- ^ Brook-Shepherd 283
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 109
- ^ Brook-Shepherd 292
- ^ Ryschka, Birgit (1 January 2008). Constructing and Deconstructing National Identity: Dramatic Discourse in Tom Murphy's The Patriot Game and Felix Mitterer's In Der Löwengrube. Peter Lang. ISBN 978-3-631-58111-7.
- ^ a b Lonnie Johnson 112-113
- ^ Robert Gellately, Social Outsiders in Nazi Germany, (2001), p. 216
- ^ 1938 German election and referendum
- ^ Evan Burr Bukey, Hitler's Austria: Popular Sentiment in the Nazi Era, 1938–1945, p. 33
- ^ Ian Kershaw (2001) Hitler 1936-1945" Nemesis, p.83
- ^ Roderick Stackelberg, Hitler's Germany: Origins, Interpretations, Legacies, p.170
- ^ "DÖW – Erkennen – Ausstellung – 1938 – Die Verfolgung der österreichischen Juden". www.doew.at. Archived from the original on 6 July 2022. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ "Jüdische Gemeinde – Wien (Österreich)". www.xn—jdische-gemeinden-22b.de. Archived from the original on 10 June 2022. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ "Jewish Vienna". www.wien.gv.at. Archived from the original on 16 April 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Riedl, Joachim (12 March 2018). "Hitlers willige Vasallen". Die Zeit. Archived from the original on 5 May 2022. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Wolfgang Häusler, Das Jahr 1938 und die österreichischen Juden. In: Dokumentationsarchiv des österreichischen Widerstandes: "Anschluß" 1938. Vienna, 1988.
- ^ Elisabeth Boeckl-Klamper, Thomas Mang, Wolfgang Neugebauer, Gestapo-Leitstelle Wien 1938–1945. Vienna 2018, ISBN 978-3-9024-9483-2, pp. 299–305; James Longo, Hitler and the Habsburgs: The Fuhrer's Vendetta Against the Austrian Royals (2018); Stephan Baier, Eva Demmerle, Otto von Habsburg. Die Biografie. Amalthea, Wien 2002, ISBN 978-3-8500-2486-0, p. 122.
- ^ Jelavich, Barbara (2008). Modern Austria: Empire and Republic, 1815–1986. Cambridge University Press. p. 227. ISBN 978-0-521-31625-5.
- ^ Schmitz-Berning, Cornelia (2007). Vokabular des Nationalsozialismus (in German). de Gruyter. p. 24. ISBN 978-3-11-019549-1.
- ^ a b David Art (2006) "The politics of the Nazi past in Germany and Austria" Cambridge University Press p.43 ISBN 9780521856836
- ^ Ian Wallace (1999) "German-speaking exiles in Great Britain" Rodopi p.81 ISBN 9789042004153
- ^ Österreichische Historikerkommission, Schlussbericht der Historikerkommission der Republik Österreich. Volume 1, 2003, pp 85.
- ^ Norbert Schausberger, Rüstung in Österreich 1938–1945, Vienna (1970).
- ^ "Hitlers Schuldendiktat: Wie Hitlers Kriegswirtschaft wirklich lief". profil.at. 26 July 2010. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Zwangsarbeit für die Rüstungsindustrie". www.mauthausen-memorial.org. KZ-Gedenkstätte Mauthausen. Archived from the original on 16 April 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Karl Glanz (2020) Die Sozialdemokratie p 28
- ^ Christoph Thurner (2017) The CASSIA Spy Ring in World War II Austria: A History of the OSS's Maier-Messner Group p. 35.
- ^ Elisabeth Boeckl-Klamper, Thomas Mang, Wolfgang Neugebauer, (2018) Gestapo-Leitstelle Wien 1938–1945 ISBN 9783902494832 p 299-305
- ^ Hansjakob Stehle, "Die Spione aus dem Pfarrhaus (German: The spies from the rectory)". In: Die Zeit, 5 January 1996
- ^ a b Lonnie Johnson 135-136
- ^ Rüdiger Overmans (2000) Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg Oldenbourg
- ^ Anschluss and World War II Archived 20 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Britannica Online Encyclopedia.
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 137
- ^ Manfried Rauchensteiner, Der Sonderfall. Die Besatzungszeit in Österreich 1945 bis 1955 (The Special Case. The Time of Occupation in Austria 1945 to 1955), edited by Heeresgeschichtliches Museum / Militärwissenschaftliches Institut (Museum of Army History / Institute for Military Science), Vienna 1985
- ^ Gunter Bischof, ed. (2020). Austria in the Nineteen Fifties. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-000-67584-9.
- ^ a b Lonnie Johnson 153
- ^ "The Austrian National Day". Austrian Embassy, Washington. Archived from the original on 25 October 2018. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 139
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 165
- ^ "Kurt Waldheim | president of Austria and secretary-general of the United Nations". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 26 September 2018. Retrieved 25 September 2018.
- ^ Brook-Shepherd 447,449
- ^ "Signatures of Partnership for Peace Framework Document". North Atlantic Treaty Organization. 5 October 2006. Archived from the original on 29 November 2006. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ^ "Press corner". European Commission – European Commission. Archived from the original on 4 February 2022. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 17, 142
- ^ "Bundesministerium für Inneres – Elections Compulsory voting". Bmi.gv.at. Archived from the original on 3 November 2007. Retrieved 3 January 2009.
- ^ "The Austrian Parliament" (PDF). Parlament.gv.at. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 April 2022. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ "Willkommen beim Österreich Konvent". Konvent.gv.at. Archived from the original on 4 January 2009. Retrieved 21 November 2008.
- ^ "24 November 2002 General Election Results – Austria Totals". Election Resources on the Internet. 2006. Archived from the original on 7 July 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2009.
- ^ "October 1st, 2006 General Election Results – Austria Totals". Election Resources on the Internet. 2006. Archived from the original on 7 July 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2009.
- ^ "Austrian far-right leader Jörg Haider dies in car crash". TheGuardian.com. 11 October 2008. Archived from the original on 21 June 2012. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "Election Resources on the Internet: Federal Elections in Austria – Nationalrat Results Lookup". www.electionresources.org. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche (17 May 2016). "Austria's Christian Kern sworn in as new chancellor | DW | 17 May 2016". DW.COM. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche (26 January 2017). "Van der Bellen takes office as Austrian president | DW | 26 January 2017". DW.COM. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche (15 October 2017). "Austrian elections: Sebastian Kurz becomes youngest leader". DW.COM. Archived from the original on 9 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Muted protests in Vienna as far-right ministers enter Austria's government". the Guardian. 18 December 2017. Archived from the original on 9 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Austrian government collapses after far-right minister fired". the Guardian. 20 May 2019. Archived from the original on 25 November 2020. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Austrian elections: support for far-right collapses". the Guardian. 29 September 2019. Archived from the original on 9 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Sebastian Kurz: Austrian leader resigns amid corruption inquiry". BBC News. 9 October 2021. Archived from the original on 9 October 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche (6 December 2021). "Austria: Karl Nehammer sworn in as new chancellor | DW | 6 December 2021". DW.COM. Archived from the original on 12 April 2022. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "Austria blocks Schengen accession of Romania and Bulgaria, while Croatia gets green light". euronews. 9 December 2022. Archived from the original on 10 February 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- ^ "Romania Recalls Ambassador Hurezeanu From Austria. MAE: Relations Will Be Diminished". Romania Journal. 9 December 2022. Archived from the original on 17 February 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- ^ "Romanians started boycott against Austrian companies". The Conservative. 21 December 2022. Archived from the original on 17 February 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- ^ "Austria's Permanent Neutrality". New Austrian Information. 16 December 2015. Archived from the original on 13 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons". United Nations Treaty Collection. 6 July 2019. Archived from the original on 6 August 2019. Retrieved 8 August 2019.
- ^ "122 countries adopt 'historic' UN treaty to ban nuclear weapons". CBC News. 7 July 2017. Archived from the original on 14 August 2019. Retrieved 8 August 2019.
- ^ Prodhan, Georgina (20 January 2013). "Neutral Austria votes to keep military draft". Reuters. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "Defence Data". europa.eu. Archived from the original on 3 June 2014. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ^ "Austria 1920 (reinst. 1945, rev. 2013)". Constitute. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "2024 Global Peace Index" (PDF).
- ^ "Eurostat – Data Explorer". Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ "Statistik Austria – Bevölkerung zu Jahresbeginn 2002–2017 nach Gemeinden (Gebietsstand 1.1.2017)". Archived from the original on 22 March 2018. Retrieved 9 July 2018.
- ^ "Alps". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 11 June 2009. Archived from the original on 1 June 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2009.
- ^ "Geography – Permanent Mission of Austria to the United Nations – Vienna". Archived from the original on 8 February 2023. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- ^ Terms and Definitions FRA 2025 Forest Resources Assessment, Working Paper 194. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023.
- ^ "Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Austria". Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; Olson, David; Joshi, Anup; Vynne, Carly; Burgess, Neil D.; Wikramanayake, Eric; Hahn, Nathan; Palminteri, Suzanne; Hedao, Prashant; Noss, Reed; Hansen, Matt; Locke, Harvey; Ellis, Erle C; Jones, Benjamin; Barber, Charles Victor; Hayes, Randy; Kormos, Cyril; Martin, Vance; Crist, Eileen; Sechrest, Wes; Price, Lori; Baillie, Jonathan E. M.; Weeden, Don; Suckling, Kierán; Davis, Crystal; Sizer, Nigel; Moore, Rebecca; Thau, David; Birch, Tanya; Potapov, Peter; Turubanova, Svetlana; Tyukavina, Alexandra; de Souza, Nadia; Pintea, Lilian; Brito, José C.; Llewellyn, Othman A.; Miller, Anthony G.; Patzelt, Annette; Ghazanfar, Shahina A.; Timberlake, Jonathan; Klöser, Heinz; Shennan-Farpón, Yara; Kindt, Roeland; Lillesø, Jens-Peter Barnekow; van Breugel, Paulo; Graudal, Lars; Voge, Maianna; Al-Shammari, Khalaf F.; Saleem, Muhammad (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T. D.; Jones, K. R.; Beyer, H. L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J. C.; Robinson, J. G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H. M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P. R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P.; Goldman, E.; Goetz, S.; Hansen, A.; Hofsvang, E.; Jantz, P.; Jupiter, S.; Kang, A.; Langhammer, P.; Laurance, W. F.; Lieberman, S.; Linkie, M.; Malhi, Y.; Maxwell, S.; Mendez, M.; Mittermeier, R.; Murray, N. J.; Possingham, H.; Radachowsky, J.; Saatchi, S.; Samper, C.; Silverman, J.; Shapiro, A.; Strassburg, B.; Stevens, T.; Stokes, E.; Taylor, R.; Tear, T.; Tizard, R.; Venter, O.; Visconti, P.; Wang, S.; Watson, J. E. M. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ Beck, Hylke E.; Zimmermann, Niklaus E.; McVicar, Tim R.; Vergopolan, Noemi; Berg, Alexis; Wood, Eric F. (30 October 2018). "Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution". Scientific Data. 5: 180214. Bibcode:2018NatSD...580214B. doi:10.1038/sdata.2018.214. ISSN 2052-4463. PMC 6207062. PMID 30375988.
- ^ "Average Conditions, Vienna, Austria". British Broadcasting Corporation. 2006. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 24 May 2009.
- ^ a b "Austrian Meteorological Institute". Archived from the original on 12 August 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ "Climate-Data.org". Archived from the original on 15 April 2017. Retrieved 15 April 2017.
- ^ Zampieri, Matteo; Scoccimarro, Enrico; Gualdi, Silvio (2013). "Atlantic influence on the Alps". Environmental Research Letters. 8 (3): 034026. Bibcode:2013ERL.....8c4026Z. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/8/3/034026.
- ^ IEA (18 November 2021). "Austria Climate Resilience Policy Indicator". IEA. Retrieved 9 December 2024.
- ^ Climate Change Post. "Austria: Climate change". www.climatechangepost.com. Retrieved 9 December 2024.
- ^ Olefs, M.; Formayer, H.; Gobiet, A.; Marke, T.; Schöner, W.; Revesz, M. (1 June 2021). "Past and future changes of the Austrian climate – Importance for tourism". Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism. Editorial: Tourism and Climate Change – an integrated look at the Austrian case. 34: 100395. doi:10.1016/j.jort.2021.100395. ISSN 2213-0780.
- ^ "2024 Environmental Performance Index". Environmental Performance Index. Retrieved 15 October 2024.
- ^ "2024 Environmental Performance Index - Austria". Environmental Performance Index. Retrieved 15 October 2024.
- ^ "Real GDP Gwoth". International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 14 November 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2023.
- ^ "GDP Growth – Expenditure Side by the Oesterreichische Nationalbank". Archived from the original on 4 December 2023. Retrieved 4 December 2023.
- ^ "OEC Austria (AUT) Exports, Imports, and Trade Partners". atlas.media.mit.edu. Archived from the original on 13 March 2016. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ Groendahl, Boris (15 February 2014). "Hypo Alpe Debt Cut Four Steps as Insolvency Not Ruled Out". Bloomberg.com. Archived from the original on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ Groendahl, Boris (17 February 2014). "Faymann Evokes 1931 Austria Creditanstalt Crash on Hypo Alpe". Bloomberg.com. Archived from the original on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ Mark (16 November 2010). "Mark's Market Analysis". Marksmarketanalysis.com. Archived from the original on 14 July 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ "Statistics on Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)". Imaa-institute.org. Archived from the original on 26 July 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ "Statistics on Mergers & Acquisitions". Imaa-institute.org. Archived from the original on 26 July 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ Ramsey, Jonathon (8 December 2009). "Volkswagen takes 49.9 percent stake in Porsche AG". Autoblog.com. Archived from the original on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ [1] Archived 9 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "TOURISMUS IN ÖSTERREICH 2007" (PDF) (in German). BMWA, WKO, Statistik Austria. May 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2008. Retrieved 18 November 2008.
- ^ a b "UNTWO World Tourism Barometer, Vol.6 No.2" (PDF). UNTWO. June 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 October 2008. Retrieved 18 November 2008.
- ^ Lonnie Johnson 168–169
- ^ "Austria Renewable Energy Fact Sheet" (PDF). Europe's Energy Portal. 23 January 2008. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 June 2009. Retrieved 20 May 2009.
- ^ "Renewable energy in Europe". Europe's Energy Portal. 2006. Archived from the original on 20 May 2009. Retrieved 20 May 2009.
- ^ a b "Country Trends". Global Footprint Network. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ^ a b c "Population at beginning of year/quarter". Statistic Austria. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ "Turkey's ambassador to Austria prompts immigration spat". BBC News. 10 November 2010. Archived from the original on 19 September 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2019.
- ^ "Mehr als ein Viertel der Bevölkerung hat Wurzeln im Ausland" (PDF) (in German). Statistik Austria. 24 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2024.
- ^ "Austria". European Commission. Archived from the original on 6 October 2023. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- ^ "Bevölkerung" (in German). Statistik Austria. Archived from the original on 19 March 2015. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- ^ Roser, Max (2014), "Total Fertility Rate around the world over the last two centuries", Our World in Data, Gapminder Foundation, archived from the original on 2 May 2023, retrieved 2 May 2023
- ^ "Eurostat – Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 27 May 2016. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ^ "Median age". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 23 May 2021. Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- ^ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Archived from the original on 28 May 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ^ "Population Forecasts" (PDF). Statistik Austria. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 November 2022. Retrieved 30 November 2022.
- ^ "Bundes-Verfassungsgesetz Art. 8 (Austrian Constitution)" (in German). 23 November 2023. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 26 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Die Bevölkerung nach Umgangssprache, Staatsangehörigkeit und Geburtsland" (PDF). Statistik Austria. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 November 2010. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ^ Keyserlingk, Robert H. (1 July 1990). Austria in World War II: An Anglo-American Dilemma. McGill-Queen's Press. pp. 138ff. ISBN 978-0-7735-0800-2. Archived from the original on 28 September 2015. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ^ Thaler, Peter (2001). The Ambivalence of Identity: The Austrian Experience of Nation-Building in a Modern Society. Purdue University Press. pp. 72ff. ISBN 978-1-55753-201-5. Archived from the original on 28 September 2015. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ^ Wodak, Ruth (2009). The Discursive Construction of National Identity. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 56ff. ISBN 978-0-7486-3734-8. Archived from the original on 28 September 2015. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ^ "Österreicher fühlen sich heute als Nation". Derstandard.at. 12 March 2008. Archived from the original on 10 October 2012. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
- ^ Minahan, James (2000). One Europe, many nations: a historical dictionary of European national groups. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 769. ISBN 978-0-313-30984-7. Archived from the original on 21 March 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2013.
- ^ Cole, Jeffrey. Ethnic groups of Europe. p. 23.
- ^ "Austria – people and society – ethnic groups". CIA – The world fact book. Archived from the original on 10 January 2021. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ "World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples – Austria: Turks" Archived 29 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Minority Rights Group International, World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples – Austria: Turks, 2008. Online. UNHCR Refworld
- ^ "Beč: Božić na gastarbajterski način | Evropa | Deutsche Welle | 07.01.2010". Dw-world.de. Archived from the original on 4 November 2013. Retrieved 25 April 2010.
- ^ Palić, Svetlana (17 July 2011). "Četiri miliona Srba našlo uhlebljenje u inostranstvu". Blic. Archived from the original on 26 October 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
Austriji (300.000)
- ^ "Serben-Demo eskaliert in Wien". 20 Minuten. 20 Minuten Online. 2008. Archived from the original on 23 February 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ^ "Srbi u Austriji traže status nacionalne manjine". Blic. 2 October 2010. Archived from the original on 9 January 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
"Srba u Austriji ima oko 300.000, po brojnosti su drugi odmah iza Austrijanaca i više ih je od Slovenaca, Mađara i Gradištanskih Hrvata zajedno, koji po državnom ugovoru iz 1955. godine imaju status nacionalne manjine u Austriji", navodi se u saopštenju.
- ^ "HKDC Geschichte – Frame". Croates.at. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 21 November 2008.
- ^ a b c d "Religionszugehörigkeit 2021: drei Viertel bekennen sich zu einer Religion" [2021 religious affiliation: three fourths profess a religion] (PDF) (with comparative data from the censuses from 1951 to 2021). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 August 2022.
- ^ a b Zulehner, Paul M. (2004). "Religion in Austria" (PDF). In Bischof, Günter; Pelinka, Anton; Denz, Hermann (eds.). Religion in Austria. Contemporary Austrian Studies. Vol. 13. Taylor & Francis. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-7658-0823-3. Archived from the original on 12 March 2024. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ^ Potančoková, Michaela; Berghammer, Caroline (2012). "Urban Faith: Religious Change in Vienna and Austria, 1986–2013" (PDF). In Hödl, Hans Gerald; Pokorny, Lukas (eds.). Religion in Austria. Vol. 2. Praesens Verlag. pp. 219, 230. ISBN 978-3-7069-0763-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d "Census 2001: Population 2001 according to religious affiliation and nationality" (PDF) (in German). Statistik Austria. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 November 2007. Retrieved 17 December 2007.
- ^ "Platz drei für die Zahl der Kirchen-Austritte". 18 September 2024.
- ^ Church data Archived 16 January 2013 at the Wayback Machine retrieved 14 January 2015
- ^ Zahl der Muslime in Österreich seit 2001 verdoppelt Archived 20 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine diepresse.com, 4 August 2017.
- ^ "Fast Facts—Austria". Jehovah's Witnesses (JW.ORG). Archived from the original on 18 May 2022. Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- ^ "Special Eurobarometer, biotechnology, page 204" (PDF) (Fieldwork: Jan–Feb 2010 ed.). Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 December 2010. Retrieved 21 February 2013.
- ^ "Studying in Austria: Tuition Fee". Help.gv.at. 1 January 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- ^ "HÖHE DES ÖH-BEITRAGES?". www.oeh.ac.at (in German). Archived from the original on 3 March 2020. Retrieved 3 March 2020.
- ^ "STC Health Index". globalresidenceindex.com. Archived from the original on 5 September 2022. Retrieved 5 September 2022.
- ^ State of Health in the EU; Companion Report 2021. Publications Office of the European Union. 2022. ISBN 978-92-76-45885-2.
- ^ "Austria: Health System Personnel". World Health Systems Facts. Archived from the original on 5 September 2022. Retrieved 5 September 2022.
- ^ "Austria - Music, Art, Theater | Britannica". Archived from the original on 18 February 2024. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ a b "Joseph Haydn | Biography, Compositions, & Facts | Britannica". 23 January 2024. Archived from the original on 31 October 2023. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Michael Haydn | Austrian composer, symphonies, operas | Britannica". Archived from the original on 3 July 2019. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Franz Liszt | Biography, Music, Compositions, Famous Works, Children, & Facts | Britannica". 16 February 2024. Archived from the original on 27 November 2023. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Franz Schubert | Biography, Music, & Facts | Britannica". 27 January 2024. Archived from the original on 19 December 2023. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Anton Bruckner | Austrian Composer & Romantic Symphony Writer | Britannica". 19 February 2024. Archived from the original on 30 November 2023. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Arnold Schoenberg | Biography, Compositions, & Facts | Britannica". March 2024. Archived from the original on 13 June 2015. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Anton Webern | Austrian Composer & 12-Tone Pioneer | Britannica". Archived from the original on 7 March 2024. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart | Biography, Music, the Magic Flute, & Facts | Britannica". 8 February 2024. Archived from the original on 5 July 2022. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ a b c "Vienna - Culture, Music, Art | Britannica". Archived from the original on 18 February 2024. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ Rockwell, John (17 July 1989). "Herbert von Karajan Is Dead; Musical Perfectionist was 81". The New York Times. pp. A1. Archived from the original on 12 July 2018. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ World Intellectual Property Organization (2024). Global Innovation Index 2024: Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship. World Intellectual Property Organization. p. 18. doi:10.34667/tind.50062. ISBN 978-92-805-3681-2. Retrieved 6 October 2024.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ "RTD – Item". ec.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 2 September 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index". INSEAD Knowledge. 28 October 2013. Archived from the original on 2 September 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ Jones, Lora (13 April 2018). "Coffee: Who grows, drinks and pays the most?". BBC News. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018. Retrieved 13 May 2018.
- ^ "Gruner Veltliner Wine". Wine-Searcher. Archived from the original on 1 March 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ^ "Zweigelt Wine". Wine-Searcher. Archived from the original on 7 February 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ^ Horak, Roman; Spitaler, Georg (2003). "Sport, Space and National Identity: Soccer and Skiing as Formative Forces: On the Austrian Example". American Behavioral Scientist. 46 (11): 1508–1518. doi:10.1177/0002764203046011004. S2CID 144319167.
- ^ "YOG Innsbruck 2012: Relive the announcement". International Olympic Committee. 12 December 2008. Archived from the original on 16 December 2008. Retrieved 24 December 2008.
- ^ "Österreichischer Fußballbund". ÖFB (in German). 2009. Archived from the original on 28 June 2009. Retrieved 17 June 2009.
- ^ Marschick, Matthias (Summer 2011). "Austrian Sport and the Challenges of Its Recent Historiography". Journal of Sport History. 38 (2): 189–198. doi:10.5406/jsporthistory.38.2.189. JSTOR 10.5406/jsporthistory.38.2.189. S2CID 145300546.
- ^ Norden, Gilbert (Spring 2001). "Austrian Sport Museums" (PDF). Journal of Sport History. 28 (1): 87–107. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 January 2017. Retrieved 3 January 2017.
Bibliography
- Brook-Shepherd, Gordon (1998). The Austrians: a thousand-year odyssey. New York: Carroll & Graf Publishers, Inc. ISBN 978-0-7867-0520-7.
- Jelavich, Barbara (1987). Modern Austria: empire and republic 1815–1986. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-31625-5.
- Johnson, Lonnie (1989). Introducing Austria: a short history. Riverside, Calif.: Ariadne Press. ISBN 978-0-929497-03-7.
- Rathkolb, Oliver. The Paradoxical Republic: Austria, 1945–2005 (Berghahn Books; 2010, 301 pages). Translation of 2005 study of paradoxical aspects of Austria's political culture and society.
- Thaler, Peter (2001). The Ambivalence of Identity: The Austrian Experience of Nation-Building in a Modern Society. West Lafayette, Ind.: Purdue University Press. ISBN 978-1-55753-201-5.
External links
- Austria. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Austria. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Austria. Information from the United States Department of State.
- Austria at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Information on Austria. Sorted by regions. Choose from 5 languages.
- Austria profile from the BBC News
 Wikimedia Atlas of Austria
Wikimedia Atlas of Austria Geographic data related to Austria at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Austria at OpenStreetMap- Key Development Forecasts for Austria from International Futures
Government
- Federal Chancellery of Austria. Official government portal.
- AEIOU Austria Albums. Archived 2 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine (in German, English).
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- Austrian Law. Information on Austrian Law.
Trade
Travel
- Austria.info. Official homepage of the Austrian National Tourist Office.
- TourMyCountry.com. Website on Austrian culture, cuisine and tourist attractions.
- Europe Pictures – Austria Archived 2 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- Austria
- Countries and territories where German is an official language
- Countries in Europe
- Federal constitutional republics
- Landlocked countries
- Member states of the European Union
- Member states of the Three Seas Initiative
- Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean
- Member states of the United Nations
- Nuclear-free zones
- OECD members
- States and territories established in 1955