Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
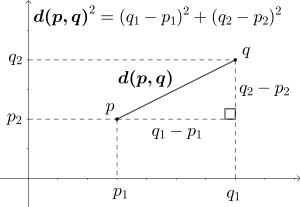
Selected image –
Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that despite a mathematical model deeming the ice cream bar flavour Goody Goody Gum Drops impossible, it was still created?
- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
- ... that subgroup distortion theory, introduced by Misha Gromov in 1993, can help encode text?
- ... that people in Madagascar perform algebra on tree seeds in order to tell the future?
- ... that ten-sided gaming dice have kite-shaped faces?
- ... that the discovery of Descartes' theorem in geometry came from a too-difficult mathematics problem posed to a princess?
- ... that Ukrainian baritone Danylo Matviienko, who holds a master's degree in mathematics, appeared as Demetrius in Britten's opera A Midsummer Night's Dream at the Oper Frankfurt?
- ... that The Math Myth advocates for American high schools to stop requiring advanced algebra?
More did you know –

- ...that a cyclic cellular automaton is a system of simple mathematical rules that can generate complex patterns mixing random chaos, blocks of color, and spirals?
- ...that a nonconvex polygon with three convex vertices is called a pseudotriangle?
- ...that the axiom of choice is logically independent of the other axioms of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory?
- ...that the Pythagorean Theorem generalizes to any three similar shapes on the three sides of a right-angled triangle?
- ...that the orthocenter, circumcenter, centroid and the centre of the nine-point circle all lie on one line, the Euler line?
- ...that an arbitrary quadrilateral will tessellate?
- ...that it has not been proven whether or not every even integer greater than two can be expressed as the sum of two primes?
Selected article –
 |
| Fractals arise in surprising places, in this case, the famous Collatz conjecture in number theory. Image credit: Pokipsy76 |
A fractal is "a rough or fragmented geometric shape that can be subdivided in parts, each of which is (at least approximately) a reduced-size copy of the whole". The term was coined by Benoît Mandelbrot in 1975 and was derived from the Latin fractus meaning "broken" or "fractured".
A fractal as a geometric object generally has the following features:
- It has a fine structure at arbitrarily small scales.
- It is too irregular to be easily described in traditional Euclidean geometric language.
- It is self-similar (at least approximately or stochastically).
- It has a Hausdorff dimension which is greater than its topological dimension (although this requirement is not met by space-filling curves such as the Hilbert curve).
- It has a simple and recursive definition.
Because they appear similar at all levels of magnification, fractals are often considered to be infinitely complex (in informal terms). Natural objects that approximate fractals to a degree include clouds, mountain ranges, lightning bolts, coastlines, and snow flakes. However, not all self-similar objects are fractals—for example, the real line (a straight Euclidean line) is formally self-similar but fails to have other fractal characteristics. Fractals, when zoomed in, will keep showing more and more of itself, and it keeps going for infinity. (Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
| General | Foundations | Number theory | Discrete mathematics |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Algebra | Analysis | Geometry and topology | Applied mathematics |
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus


![Image 1 Rejewski, c. 1932 Marian Adam Rejewski (Polish: [ˈmarjan rɛˈjɛfskʲi] ⓘ; 16 August 1905 – 13 February 1980) was a Polish mathematician and cryptologist who in late 1932 reconstructed the sight-unseen German military Enigma cipher machine, aided by limited documents obtained by French military intelligence. Over the next nearly seven years, Rejewski and fellow mathematician-cryptologists Jerzy Różycki and Henryk Zygalski, working at the Polish General Staff's Cipher Bureau, developed techniques and equipment for decrypting the Enigma ciphers, even as the Germans introduced modifications to their Enigma machines and encryption procedures. Rejewski's contributions included the cryptologic card catalog and the cryptologic bomb. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)